文献:Improving Drug Delivery of Micellar Paclitaxel against Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer by Coloading Itraconazole as a Micelle Stabilizer and a Tumor Vascular Manipulator
文献链接:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30444572/
作者:Ling Zhang, Zhengsheng Liu, Chao Kong, Chun Liu, Kuan Yang, Huijun Chen, Jinfeng Huangand Feng Qian
相关产品:FITC-PEG-PLA-RB 荧光素-聚乙二醇-聚乳酸-罗丹明B
原文摘要:Although polymeric micelles of paclitaxel (PTX) significantly reduce excipient-induced toxicity compared with Taxol, they exhibit few clinical advantages in tumor inhibition and overall survival. To improve, itraconazole (ITA), an antifungal drug with potent anti-angiogenesis activity, is co-encapsulated together with PTX within the PEG-PLA micelles. The strong intermolecular interactions between the payloads inhibit drug crystallization and prevent drugs from binding with external proteins, render super stable micelles upon dilution and exposure to biological environment, and enter the tumor cells through endocytosis. The co-encapsulated micelles show strong anti-proliferation potency against non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and even PTX resistant NSCLC cells in vitro and significantly improve the drug accumulation within the tumor in vivo. Compared with PTX monotherapy or combination therapy using individual PTX and ITA micelles, the co-encapsulated micelle demonstrates strikingly superior efficacy in tumor growth inhibition, recurrence prevention, and reversion of PTX resistance, in Kras mutant patient derived xenografts,orthotropic models, and paclitaxel-resistance subcutaneous models. Besides the pharmacokinetic improvement, therapeutic benefits are also contributed by angiogenesis inhibition and blood vessel normalization by ITA. Utilizing the pharmaceutical and pharmacological synergies between the therapeutic agents, a simple yet effective design of a combination cancer nanomedicine that is industrially scalable and clinically translatable is achieved.
FITC - PEG - PLA - RB融合了多种功能基团。FITC(异硫氰酸荧光素)赋予其出色的荧光性能,可用于生物成像和检测,能够有效标记和追踪生物分子或材料在生物体内的行为。PLA 具备良好的生物可降解性,在生物医学应用中可逐步降解,减少对生物体的长期不良影响。RB(罗丹明 B)则进一步增强了其荧光信号的多样性和可检测性,拓宽了在荧光分析和生物标记领域的应用范围,在化合物递送系统研究、细胞标记与追踪等生物医学相关研究中有着应用潜力。该文献设计一种PEG-PLA胶束系统的新型胶束纳米颗粒,并结合紫杉醇(PTX)和伊曲康唑(ITA)的共封装。利用双荧光标记的聚乙二醇-PLA嵌段共聚物和共聚焦激光扫描显微镜(CLSM),评估了不同胶束在与A549/PTX细胞孵育后的结果。过程如下:
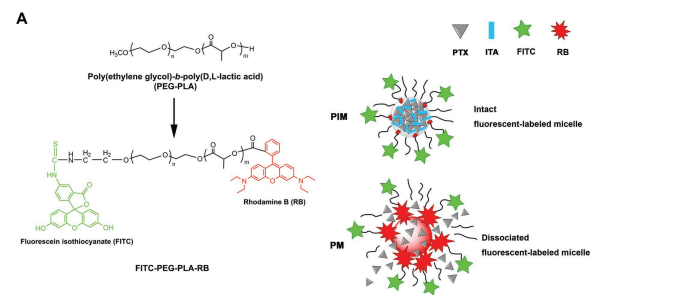
图1:双荧光胶束
将FITC - PEG - PLA - RB偶联与未标记的PEG-PLA结合,构建了双荧光胶束(图1)。标记胶束的直径与未标记胶束的直径相似。完整的荧光胶束仅从壳共轭染料(FITC)发出绿色荧光,而核心共轭红色染料(RB)由于其高核心密度而被自猝灭。当胶束解离后,PLA-RB的荧光被猝灭,红色荧光信号可检测到。经过长时间的孵育,所有胶束中壳结合的绿色FITC增加,胶束内吞作用增加。PTX负载的PM组表现出更强的核心共轭红色RB强度,表明比空白胶束(BM)或PIM有更多的胶束解离。
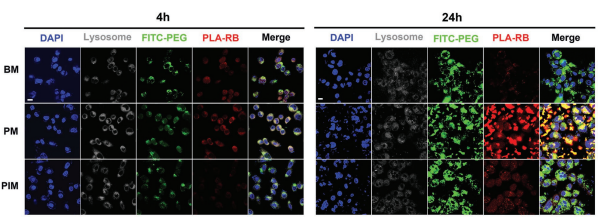
图2:荧光标记的PEG-PLA胶束在4和24小时孵育后细胞内运输的CLSM图像
结论:通过FITC - PEG - PLA - RB参与评估PEG-PLA胶束在与A549/PTX细胞孵育后的结果,得到有效载荷对生物介质中胶束稳定性的影响: (1)尽管PM和BM的CMC值相同,但PTX的加载降低了胶束在细胞培养环境中的稳定性,可能是由于PTX与细胞质蛋白结合的强烈倾向(2)虽然PTX和ITA都有很强的蛋白质结合能力,但两者之间的强分子间相互作用有效地阻碍了它们从PIM的释放、与细胞质蛋白的竞争性结合以及随后胶束的破坏。

 2025-08-21 作者:ZJ 来源:
2025-08-21 作者:ZJ 来源:

