文献:PEGylated WS2 nanodrug system with erythrocyte membrane coating for
chemo/photothermal therapy of cervical cancer
文献链接:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32812542/
作者:Ying Long, Xianjin Wu, Zhen Li , Jialong Fan , Xing Hu, Bin Liu
相关产品:
DSPE-PEG2000-FA 磷脂-聚乙二醇2000-叶酸
LA-PEG2000-NH2 硫辛酸-聚乙二醇2000-氨基
原文摘要:The side effect of chemical drugs and multi-drug resistance are serious obstacles for hindering efficient tumor therapy. Recently, the combination of chemo/photothermal therapy (CT/PT) has been adopted to address these issues with low drug dosage. However, developing multi-functional drug delivery systems with improved immune escape capability and enhanced
drug accumulation at specific tumor tissue is still on the early stage. Herein, polyethylene glycol (PEG) modified WS2 nanosheet (WS2-PEG) was used as a nanocarrier scaffold for Doxorubicin (DOX, D) loading and near-infrared fluorescence probe indocyanine green (ICG, I) doping.After surface modification with erythrocyte membrane (M) and targeted FA molecule, a new biomimetic system (WID@M-FA NPs) with high biocompatibility, prolonged cycle time (3.6-fold longer than WID NPs) and remarkable near-infrared photothermal function was developed for targeted cervical cancer therapy. In vitro assay indicated that photothermal effects caused by ICG upon laser irradiation can not only enhance cellular uptake of drug, but also enhanced tumor cell killing efficiency, as well. Moreover, targeted accumulation of DOX at cervical cancer tissue and synergistic chemo/photothermal therapy was finally resulted in tumor elimination more than 95 % without side effect to normal tissues in vivo. These excellent preclinical data indicate that WID@M-FA NPs may be an efficient therapeutic modality for cervical cancer.
DSPE-PEG2000-FA通常为淡黄色或黄色粉末。DSPE提供了良好的亲脂性,使其能够与其他脂质或聚合物组分混合,形成靶向细胞的纳米粒子或脂质体;PEG2000增加了水溶性,并提高了生物相容性;FA具有与细胞表面受体叶酸受体的高亲和力,赋予了材料靶向性.主要应用于生物医学领域,如tumor的靶向成像和等。通过叶酸与叶酸受体的特异性结合,DSPE-PEG2000-FA能够将化合物、基因等靶向递送至tumor细胞。 该文献采用聚乙二醇(PEG)修饰的WS2纳米片(WS2-PEG)作为纳米载体支架,用于阿霉素(DOX,D)的加载和近红外荧光探针吲哚菁绿(ICG,I)的掺杂。用红细胞膜(M)和靶向FA分子进行表面修饰后,开发了一仿生系统(WID@M-FA NPs)。过程如下:
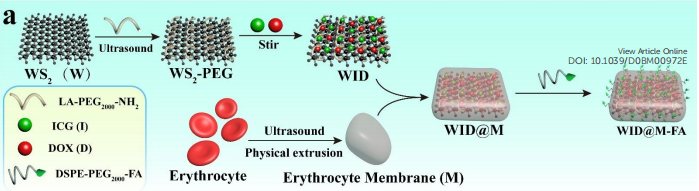
图:WID@M-FA纳米片的制备
水分散性WS2纳米颗粒(WS2-PEG NPs)的制备
采用超声辅助液相剥离法合成了水分散的WS2 NPs。将LA-PEG2000-NH2加入WS2纳米片中,在纯化水中,室温下超声处理。然后收集黄褐色水溶液,离心,得到上黄色分散体。然后收集WS2-PEG NPs,用纯化水反复洗涤,离心,去除残留的LA-PEG2000-NH2,最终得到的WS2-PEG NPs冷冻干燥。
WID@M-FA NPs的合成
WS2-PEG NPs分散在 PBS中。加入ICG后,在室温黑暗中搅拌。收集WS2-PEG-ICG NPs(WI NPs),用PBS反复洗涤,离心,除去未卸载的ICG。得到的WI NPs沉淀在PBS(pH7.4)中重新处理。加入DOX后,在室温黑暗中搅拌。最后,通过透析纯化混合物,以去除游离的DOX。制备红细胞膜(M),然后,将红细胞囊泡缓慢加入WID NPs溶液中。然后,将混合物在水浴中超声,通过聚碳酸酯多孔膜挤压,得到WID@M NPs。然后,将DSPE-PEG2000-FA与WID@M NPs溶液共孵育。然后收集WID@M-FA NPs,用PBS反复洗涤,离心,去除残留的DSPE-PEG2000-FA。
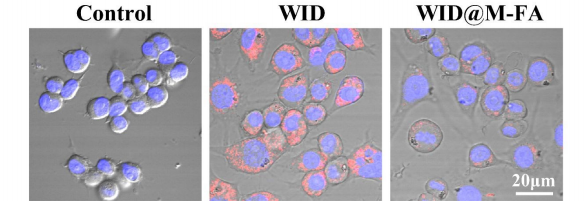
图:RAW264.7细胞与WID和WID@M-FA纳米颗粒孵育后的CLSM图像
结论:DSPE-PEG2000-FA和LA-PEG2000-NH2参与制备的仿生系统(WID@M-FA NPs),具有高生物相容性、延长周期时间(比WIDNPs长3.6倍)和的近红外光热功能并具有靶向性。体外实验表明,ICG对激光照射引起的光热效应不仅能提高细胞对化合物的摄取,还能提高tumor细胞的效率。此外,DOX在组织中的靶向积累和协同Chemotherapy /光热最终使tumor消除95 %以上,对体内正常组织无副作用。

 2025-07-30 作者:ZJ 来源:
2025-07-30 作者:ZJ 来源:

