文献:Construction of CNA35 Collagen-Targeted Phase-Changeable Nanoagents for LIFU-Triggered Ultrasound Molecular Imaging of Myocardial Fibrosis in Rabbits
文献链接:https://xueshu.baidu.com/usercenter/paper/show?paperid=16460v406v7k0g60nt1j0j30m7239159&site=xueshu_se
作者:Qin Zhou, Yalin Zeng, Qingsong Xiong, Shigen Zhong, Pan Li, Haitao Ran,Yuehui Yin, Chris P. M. Reutelingsperger, Frits W. Prinze, and Zhiyu Ling
相关产品:DSPE-PEG2000-NH2 磷脂-聚乙二醇2000-氨基
原文摘要:Myocardial fibrosis plays an important role in the development of heart failure and malignant arrhythmia, which potentially increases the incidence of sudden cardiac death. Therefore, early detection of myocardial fibrosis is of great significance for evaluating the prognosis of patients and formulating appropriate treatment strategies. Late gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging is considered as the currently effective strategy for noninvasive detection of myocardial fibrosis, but it still suffers some critical issues. In this work, a multifunctional liquid-gas
phase-changeable type I collagen-targeted fluorocarbon nanoparticles (CNA35-PFP NPs) have been elaborately designed and constructed for molecular imaging of fibrotic myocardium based on ultrasound imaging. These as-constructed CNA35-PFP NPs are intravenously infused into rabbit circulation with animal model of myocardial infarction. Especially, these targeted CNA35-PFP NPs with nanoscale size could efficiently pass through the endothelial cell gap and adhere to the surface of fibroblasts in the fibrotic myocardium. Importantly, followed by low intensity focused ultrasound (LIFU) irradiation on the myocardium, these intriguing CNA35-PFP NPs could transform from liquid into gaseous microbubbles, which further significantly enhanced the ultrasound contrast in the fibrotic area, facilitating the detection by diagnostic ultrasound imaging. Therefore, this work provides a desirable noninvasive, economical and real-time imaging technique for the assessment of cardiac fibrosis with diagnostic ultrasound based on the rational design of liquid-to-gas phase-changeable nanoplatforms
DSPE-PEG2000-NH2 是一种白色固体粉末状的活性磷脂,由二硬脂酰基磷脂酰乙醇胺(DSPE)、聚乙二醇 2000(PEG2000)和氨基(NH₂)组成,其中 DSPE 提供疏水性,PEG2000 赋予亲水性和良好的水溶性及生物相容性,氨基则可用于与其他含有羧基、酸酐、酰氯等官能团的化合物发生化学反应,实现共价键合,从而对脂质体、纳米颗粒、高分子材料等进行表面修饰,改变其表面性质. 它可用于制备接枝或聚乙二醇化脂质体、胶束等自组装试剂,还可应用于化合物释放、纳米技术、新材料研究、细胞培养、配体研究、多肽合成支持等领域。
基于此该文献设计并构建了一种多功能的I型胶原靶向氟碳纳米颗粒(CNA35-PFP NPs),用于基于超声成像的分子成像。过程如下:
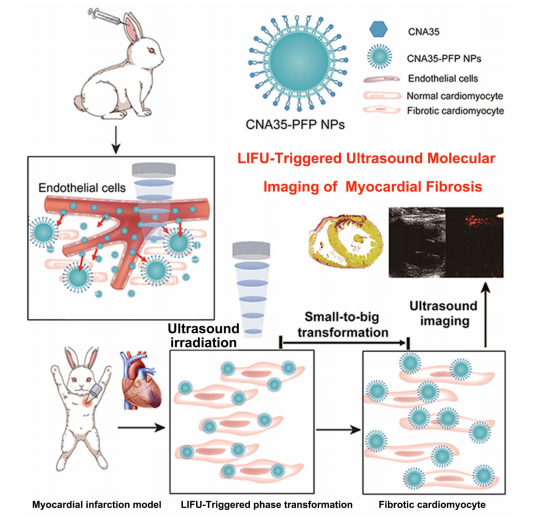
图:CNA35-PFP NPs联合LIFU检测心肌纤维化的设计示意图
DPPC、DSPE、DSPG、胆固醇溶解于三氯甲烷,然后用旋转真空蒸发器去除有机溶剂。在液体膜溶液中加入液体全氟戊烷后,用超声仪脉冲振动制备氟超声脂质纳米颗粒。最后,在冷冻离心机离心获得纳米均匀的造影剂。每次离心后,用PBS清洗PFP NPs。为了制备CNA35标记的纳米颗粒(CNA35-PFP NPs),采用了典型的碳二亚胺方法。DSPE-PEG2000-NH2在纳米颗粒合成过程中取代DSPE,并与少量DiI混合。其他步骤与上所述相同。CNA35-FITC与制备的可相纳米颗粒混合。悬液在冰浴中孵育小时,离心浓缩,用2-吗啉-乙磺酸洗涤次。整个过程都是在黑暗中进行的,以避免FITC荧光活性的损失。
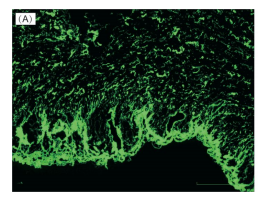
图:胶原纤维用CNA35-FITC染色,荧光共聚焦显微镜观察显示绿色荧光。
结论:DSPE-PEG2000-NH2参与制备的纳米级的靶向CNA35-PFP NPs可以有效地通过内皮细胞间隙,粘附在纤维化心肌的成纤维细胞表面。随着心肌低强度聚焦超声(LIFU)照射,这些CNA35-PFP NPs可以从液体转化为气态微泡,进一步增强了纤维化区域的超声对比度,便于超声成像的检测。

 2025-08-05 作者:ZJ 来源:
2025-08-05 作者:ZJ 来源:

