文献:Enhanced biohomogeneous composite membrane-encapsulated nanoplatform with podocyte targeting for precise and safe treatment of diabetic nephropathy
文献链接:https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acsnano.3c04671
作者:Kui Fan , Shiyi Yuan , Mi Zhou , Yuan Yu , Jing Guo , Liang Fang , Chanjuan Zhou , Peijin Cui , Siliang Zhang , Rong Li , Zhigang Wang , Ling Zhong , Li Zeng
相关产品:DSPE-mPEG 2000 -COOH(磷脂-甲氧基聚乙二醇2000-羧基)
原文摘要:
Diabetic nephropathy (DN), associated with high mobility and disability, is the leading cause of end-stage kidney disease worldwide. Dysfunction of the mammalian target of the rapamycin (mTOR) pathway and reactive oxygen species (ROS) activation in the glomeruli is the main hypnosis for DN progression. However, the use of mTOR inhibitors for DN treatment remains controversial. In this study, we built a multifunctional selective mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) inhibiting nanoplatform (naming as ESC-HCM-B) that targets the release of mTOR and ROS inhibitors near podocytes, aiming to confirm whether combination therapy is an alternative method for DN treatment. The results showed that ESC-HCM-B achieved high drug loading because of the core mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNPs), and the enhanced biohomogeneous composite membrane endowed ESC-HCM-B with the characteristics of avoiding immune phagocytosis, automatic valve-type slow-release drug, and high stability. In vitro, the nanoplatform showed high efficiency in podocyte targeting but no significant cytotoxicity or apoptotic promotion. In particular, the quantum dots carried by ESC-HCM-B further amplified the effect of “nanoenzyme”; this mechanism reduced the ROS level in podocytes induced by high glucose, protected mitochondrial damage, and restored mitochondrial energy metabolism. In vivo, the nanoplatform specifically targeted the glomerular and podocyte regions of the kidney. After treatment, the nanoplatform significantly reduced urinary protein levels and delayed glomerulosclerosis in DN rats. This nanoplatform provides a safe and effective strategy for DN treatment.
DSPE-mPEG 2000 -COOH:一种多功能的磷脂-聚乙二醇-羧基化合物。DSPE是1,2 -二硬脂酰- sn -甘油- 3 -磷酸乙醇胺(1,2 - Distearoyl - sn - glycero - 3 - phosphoethanolamine),这是一种亲脂性的磷脂成分,具有两条长的硬脂酰脂肪酸链,能够与脂质环境很好地相互作用。mPEG2000 代表甲氧基聚乙二醇(Methoxy - polyethylene glycol),其分子量约为 2000。聚乙二醇链具有良好的水溶性和生物相容性,甲氧基(- OCH₃)在一端封端,使得 PEG 链在这一端相对稳定。COOH 代表羧基(- COOH),它是一种活性官能团,为化合物提供了化学反应性。这种化合物的结构使它兼具亲脂性和亲水性。DSPE 部分提供亲脂性,mPEG2000 部分提供亲水性,而羧基则为进一步的化学修饰提供了可能。基于DSPE-mPEG 2000 -COOH 的性能,抑制纳米平台(ESC-HCM-B)的合成如下:
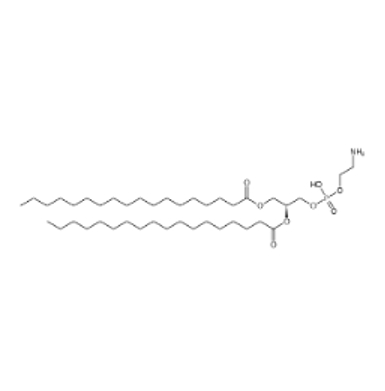
图:DSPE结构式
合成过程:
将DSPE-mPEG 2000 加入到反应容器中,随后加入适量的有机溶剂,放入磁力搅拌子,将反应容器置于磁力搅拌器上,搅拌,直至 DSPE-mPEG 2000 完全溶解,形成澄清透明的溶液。将称取好的羧基化试剂缓慢加入到上述溶液中,边加边搅拌,使其均匀分散在反应体系中。若反应需要催化剂,接着再将催化剂加入到体系中,继续搅拌,使各反应物充分混合均匀,形成初始的反应体系。若反应需要加热,将装有反应体系的容器转移至加热设备中,通过温度控制器设定好反应温度,加热,使反应体系在设定温度下进行反应。反应过程中持续搅拌,密切观察反应体系的状态变化,反应时间依据反应物的活性、浓度以及目标转化率等因素而定。对于一些需要惰性气体保护的反应,在加热反应前,可通过向反应容器中通入氮气或氩气等惰性气体,排出容器内的空气,然后在持续通入惰性气体的氛围下进行反应,气体流量可根据容器大小等因素进行适当调节。在反应过程中,可以定期取样进行分析监测。将纯化后的 DSPE-mPEG 2000 -COOH 与其他准备好的关键成分按照设计好的比例在合适的溶剂中进行混合。可以通过温和的搅拌或者超声处理等方式使各成分充分混匀,促进它们之间的相互作用,诱导自组装形成纳米平台 ESC-HCM-B。
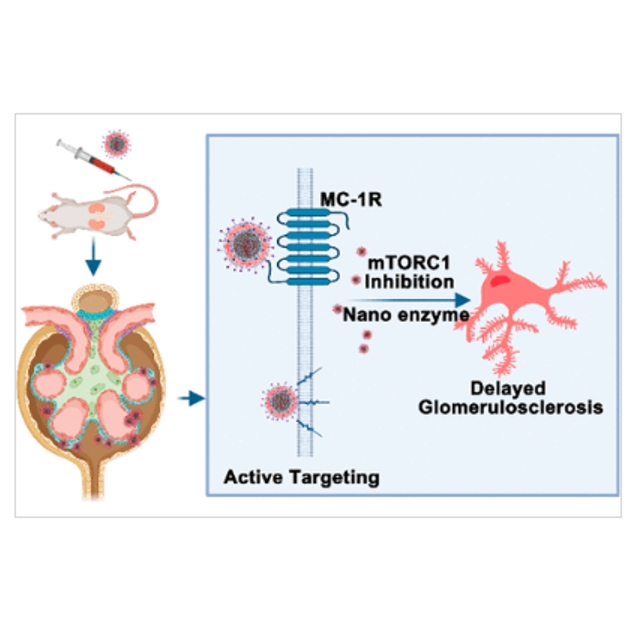 图:作用机制示意
图:作用机制示意
结论:
该文献成功制备出基于DSPE-mPEG 2000 -COOH 合成的抑制纳米平台(ESC-HCM-B)。ESC-HCM-B由于核心介孔二氧化硅纳米粒子(MSNPs)而实现了高载药量,增强的生物均质复合膜赋予了ESC-HCM-B避免免疫吞噬、自动阀式慢速释放等特性。该纳米平台为 DN heal提供了安全有效的策略。

 2025-08-08 作者:ws 来源:
2025-08-08 作者:ws 来源:

