文献:Biomimetic nano-NOS mediated local NO release for inhibiting cancer-associated platelet activation and disrupting tumor vascular barriers
文献链接:https://xueshu.baidu.com/usercenter/paper/show?paperid=1k2g00e0ar2n0a10kv190jn09h019023&site=xueshu_se
作者:Zhifang Ma, Shi Liu, Yue Ke, Haozheng Wang, Runhai Chen, Zehong Xiang, Zhigang Xie, Qiang Shi, and Jinghua Yin
相关产品:DSPE-PEG-cRGD 磷脂-聚乙二醇-cRGD肽
原文摘要:Platelets attribute to the hypercoagulation of blood and maintenance of the tumor
vascular integrity, resulting in limited intratumoral perfusion of nanoparticle into solid tumors. To overcome these adversities, we herein present an antiplatelet strategy based on erythrocyte membrane-enveloped proteinic nanoparticles that biomimic nitric oxide synthase (NOS)with co-loading of L-Arginine (LA) and photosensitizer IR783 for local NO release and inhibition of the activation of tumor-associated platelets specifically, thereby enhancing vascular permeability and accumulation of the nanoparticles in tumors. A cRGD-immobolized membrane structure is constructed to actively target platelets and cancer cells respectively, through overexpressed
integrin receptors such as integrin αIIbβ3 and αvβ3, accelerating the inhibition of platelet activation and endocytosis of nanoparticles by tumor cells. Bio-mimicking the arginine/NO pathway in vivo, synergistical delivery of LA and IR783 enables LA molecules readily oxidize to NO with O2 that is mediated by activated IR783, the resulted NO not only retards the activity of platelets to disrupt the vascular integrity of tumor but also enhances toxicity to cancer cells. In addition, NIR-controlled release localizes the NO spatiotemporally to tumor-associated platelets and prevents undesirable systemic bleeding substantially. The reduction of the hypercoagulable
state is further demonstrated by the down-regulation of tissues factor (TF) expression in tumor cells. Our study describes a promising approach to combat cancer, which advances the
biomimetic NOS system as the potent therapeutic forces toward clinic applications.
DSPE-PEG-cRGD由 DSPE、PEG 和 cRGD 三部分组成。DSPE 是常见的磷脂,可作脂质成分;PEG 是水溶性聚合物,能增加稳定性、延长循环时间;cRGD 是特异性细胞黏附分子配体,可靶向特定细胞。主要用于胶束、囊泡的被动靶向和主动靶向研究以及化合物输送,还可用于化合物传递、基因转染和生物分子修饰,能改善胶囊化合物的体内循环时间和稳定性。该文献提出了一种基于红细胞膜包膜蛋白纳米颗粒的制备策略,该策略仿生一氧化氮合酶(NOS)与l-精氨酸(LA)和光敏剂IR783相结合,用于局部NO释放,从而增强作用部位纳米颗粒的积累。
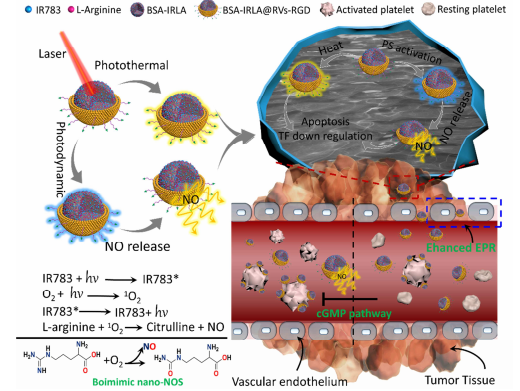
图:纳米系统原理图
制备过程如下:
通过低渗处理红细胞,使其膨胀并释放出内部内容物,然后通过离心去除血红蛋白等杂质,得到纯净的红细胞膜。将BSA蛋白、GSH、IR783和l-精氨酸溶解在PBS(pH=7.4)中搅拌,混合物超声,然后搅拌。然后,在搅拌下将乙醇缓慢滴加入上述溶液中,然后用去离子水透析反应混合物,除去乙醇和额外的反应物。BSA-IRLA复合材料离心。采用相同的方法合成了BSA-IR复合材料。将 DSPE-PEG-cRGD 与纳米颗粒结合,常用的方法包括共挤压、超声处理或微流体电穿孔等。将修饰后的纳米颗粒与红细胞膜混合,通过适当的方法使红细胞膜包裹在纳米颗粒表面,形成红细胞膜包膜蛋白纳米颗粒。对制备的红细胞膜包膜蛋白纳米颗粒进行纯化,去除未结合的物质,并通过各种技术对其进行表征,如粒径、表面电荷、稳定性等。
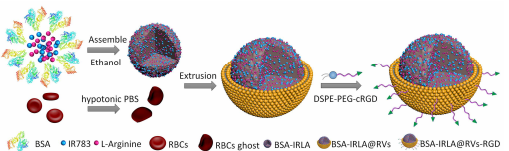
图:仿生生物BSA-IRLA@RVs-RGD的制备工艺示意图
结论:DSPE-PEG-cRGD参与制备的仿生NOS纳米平台,可有效地破坏cancer细胞。NOS纳米颗粒为共装载LA和IR783的红细胞膜包膜蛋白纳米颗粒。通过过表达整合素受体,构建crgd和固定膜结构,主动靶向cancer细胞。在NIR激光下,活化的IR783分子用ROS氧化LA侧链上的胍,NO局部在tumor周围释放。局部释放的NO增强纳米颗粒对tumor组织的灌注。

 2025-08-14 作者:ZJ 来源:
2025-08-14 作者:ZJ 来源:

