文献:‘Adhesion and release’ nanoparticle-mediated efficient inhibition of platelet activation disrupts endothelial barriers for enhanced drug delivery in tumors
文献链接:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S014296122030867X
作者:Jinxu Cao, Peng Yang, Pengzhen Wang, Shuting Xu, Yunlong Cheng, Kang Qian , Minjun Xu , Dongyu Sheng , Yixian Li , Yan Wei b,Qizhi Zhang
相关产品:Mal-PEG-NHS 马来酰亚胺-聚乙二醇-氨基
原文摘要:Activated platelets can maintain tumor vessel integrity, thereby leading to limited tumor perfusion and suboptimal antitumor efficacy of nanoparticle-based drugs. Herein, to disrupt the tumor vascular endothelial barriers by inhibiting the transformation of resting platelets to activated platelets, a TM33 peptide-modified gelatin/oleic acid nanoparticle loaded with tanshinone IIA (TNA) was constructed (TM33-GON/TNA). TM33-GON/TNA could adhere to activated platelets by specifically binding their superficial P-selectin and release TNA into the extracellular space under matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) stimulation, leading to local high TNA exposure. Thus, platelet activation, adhesion, and aggregation, which occur in the local environment around the activated platelets, were efficiently inhibited, leading to leaky tumor endothelial junctions. Accordingly, TM33-GON/TNA treatment resulted in a 3.2-, 4.0-, and 11.2-fold increase in tumor permeation of Evans blue (macromolecule marker), small-sized Nab-PTX (~10 nm), and large-sized DOX-Lip (~100 nm), respectively, without elevating drug delivery to normal tissues. Ultimately, TM33-GON/TNA plus Nab-PTX exhibited superior antitumor efficacy with minimal side effects in a murine pancreatic cancer model. In addition, the TM33-GON/TNA-induced disrupted endothelial junctions were reversibly restored after the treatment because the number of platelets was not reduced, which implies a low risk of the undesirable systemic bleeding. Hence, TM33-GON/TNA represents a clinically translational adjuvant therapy to magnify the antitumor efficacy of existing nanomedicines in pancreatic cancer and other tumors with tight endothelial lining.
Mal-PEG-NH2由马来酰亚胺(MAL)、聚乙二醇(PEG)和氨基(NH2)三个部分组成。马来酰亚胺基团位于PEG链的一端,而氨基则位于另一端。这种结构使得Mal-PEG-NH2具有双功能性质,能够与其他生物分子进行特异性反应。该文献构建一种含有丹参酮IIA(TNA)的TM33肽修饰明胶/油酸纳米颗粒(TM33-GON/TNA)。TM33-GON/TNA可通过特异性结合,在基质金属蛋白酶-2(MMP-2)刺激下,释放TNA进入细胞外空间,导致局部高TNA暴露。Mal - PEG - NHS 在 TM33 - GON/TNA 的制备过程中,可以起到连接、修饰和功能化的关键作用。
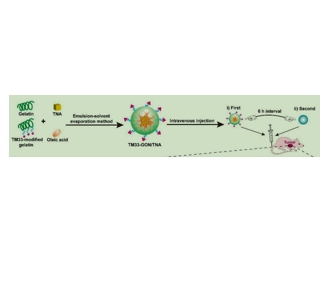
图为:TM33-GON/TNA在体内的设计特点和所提出的作用机制
Mal-PEG-NHS在TM33-GON/TNA制备中的应用:
将溶解好的 Mal - PEG - NHS 溶液缓慢滴加到含有 TM33 的反应体系中。Mal - PEG - NHS 中的马来酰亚胺(Mal)基团可以与 TM33 中可能存在的巯基(- SH)发生特异性的点击化学反应,形成稳定的共价键。反应可以在室温下进行,但为了加快反应速度,也可以在适当的温度(如 30 - 40°C)下进行,并在搅拌或振荡条件下反应一定时间(例如数小时至数十小时,具体时间可通过薄层色谱(TLC)、高效液相色谱(HPLC)等手段监测反应进程来确定)。
在完成 Mal - PEG - NHS 与 TM33 的反应后,将得到的产物加入到 GON/TNA 的分散液中。此时,Mal - PEG - NHS 中的 N - 羟基琥珀酰亚胺(NHS)基团可以与 GON/TNA 表面可能存在的氨基(- NH₂)发生反应,形成酰胺键。反应条件可与第一步类似,不过可能需要根据 GON/TNA 的性质进行适当调整。例如,如果 GON/TNA 对温度较为敏感,则反应温度需要降低。同样,可以通过适当的分析手段(如红外光谱(IR)观察官能团变化、动态光散射(DLS)监测粒径变化等)来监测反应是否完成。
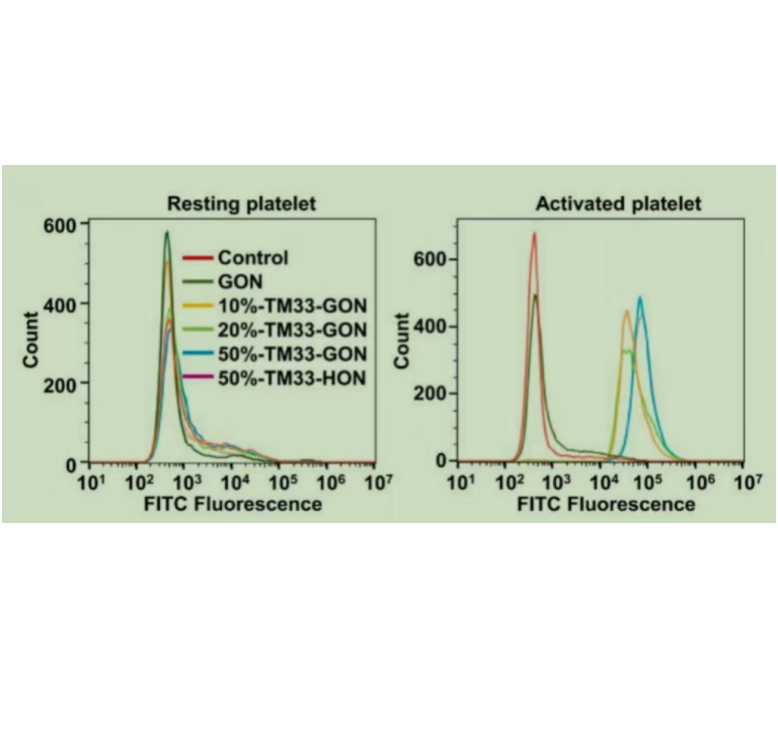
图为:体外TM33-GON与活化血小板的结合活性和TM33-GON/TNA对MMP-2的体外敏感性
结论:Mal - PEG - NHS 的马来酰亚胺(Mal)基团具有高活性,能够与含有巯基(- SH)的化合物发生特异性的迈克尔加成反应(Michael addition reaction)。假设 TM33 含有巯基,它可以与 Mal - PEG - NHS 的 Mal 基团反应,形成稳定的共价键。同时,N - 羟基琥珀酰亚胺(NHS)基团可以与含有氨基(- NH₂)的 GON/TNA 发生反应,形成酰胺键。这样,通过 Mal - PEG - NHS 作为桥梁,实现了 TM33 和 GON/TNA 的连接。PEG(聚乙二醇)链段的引入可以增加 TM33 - GON/TNA 复合物的稳定性。PEG 的柔性链可以减少复合物内部的相互作用,防止团聚。例如,当 GON/TNA 是纳米材料时,通过 Mal - PEG - NHS 连接 TM33 后,PEG 链段在纳米材料表面形成一层 “保护壳”,抑制纳米颗粒之间的聚集,从而保持复合物在溶液中的稳定性。

 2025-08-15 作者:lkr 来源:
2025-08-15 作者:lkr 来源:

