文献:Targeted nanomedicine for prostate cancer therapy: docetaxel and curcumin co-encapsulated lipid–polymer hybrid nanoparticles for the enhanced anti-tumor activity in vitro and in vivo
文献链接:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26203689/
作者:Jieke Yan, Yuzhen Wang, Xufeng Zhang, Shuangde Liu, Chuan Tian & Hongwei Wang
相关产品:
原文摘要:
Docetaxel (DTX) remains the only effective drug for prolonging survival and improving quality of life of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer(mCRPC)patients.Combination anticancer therapy encapsulating DTX and another extract of traditional Chinese medicine is one nano-sized drug delivery system promising to generate synergistic anticancer effects, to maximize the treatment effect, and to overcome multi-drug resistance. The purpose of this study is to construct lipid–polymer hybrid nanoparticles (LPNs) as nanomedicine for co-encapsulation of DTX and curcumin (CUR). Methods: DTX and CUR co-encapsulated LPNs (DTX-CUR-LPNs) were constructed. DTXCUR-LPNs were evaluated in terms of particles size, zeta potential, drug encapsulation, and drug delivery. The cytotoxicity of the LPNs was evaluated on PC-3 human prostate carcinoma cells (PC3 cells) by MTT assays. In vivo anti-tumor effects were observed on the PC3 tumor xenografts in mice. Results: The particle size of DTX-CUR-LPNs was 169.6 nm with a positive zeta potential of 35.7 mV. DTX-CUR-LPNs showed highest cytotoxicity and synergistic effect of two drugs in tumor cells in vitro. In mice-bearing PC-3 tumor xenografts, the DTX-CUR-LPNs inhibited tumor growth to a greater extent than other contrast groups, without inducing any obvious side effects. Conclusion: According to these results, the novel nanomedicine offers great promise for the dual drugs delivery to the prostate cancer cells, showing the potential of synergistic combination therapy for prostate cancer.
PEG-DSPE,特别是mPEG-DSPE,是DSPE(二硬脂酰磷脂酰乙醇胺)的一种PEG(聚乙二醇)化衍生物。在这种化合物中,PEG的末端通常因甲氧基封端而失活,无法进一步反应。PEG-DSPE在制备长循环脂质体、高分子胶束、长循环纳米粒等药物传递系统中展现出迅速的发展势头。例如,DSPE-PEG2000在制备长循环脂质体时尤为受欢迎,因为它能使脂质体避免被MPS组织捕获,从而延长在血液中的循环时间,并提升其进入病理组织的几率。
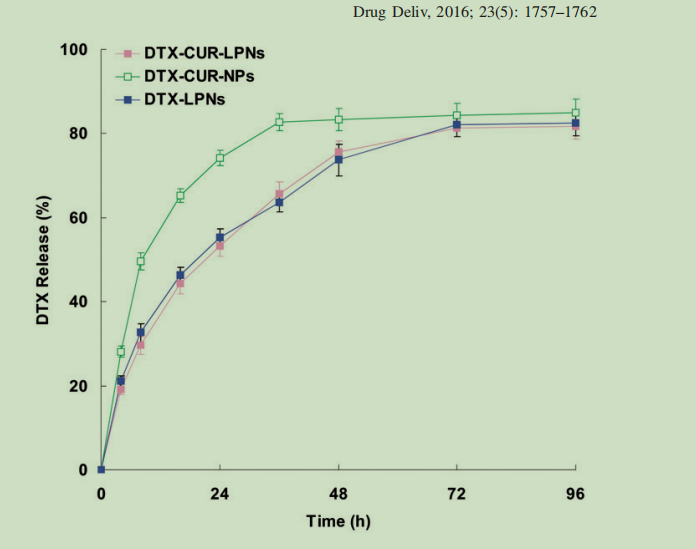
图为:不同LPNs系统的体外释放DTX。
PEG-DSPE在DTX-CUR-LPNs的制备:
DTX-CUR-LPNs采用纳米沉淀技术结合自组装制备。DTX、CUR和PLGA首先溶解在乙腈中。卵磷脂和PEG-DSPE溶解在乙醇水溶液PLGA聚合物,加热药物和PLGA乙腈溶液添加到预热脂质水溶液滴温和搅拌。让纳米颗粒在连续搅拌下自组装,同时让有机溶剂蒸发。剩余的有机溶剂和游离分子通过洗涤纳米颗粒溶液,然后在水中重悬,得到最终所需的DTX-CUR-LPNs。DTXCUR-LPNs立即使用,或储存以供以后使用。采用相同的方法制备DTX封装LPNs(DTX-LPNs)、DTX封装LPNs(CUR-LPNs)和无药物LPNs(LPNs)。DTX和CUR共封装的PLGA纳米颗粒(DTX-CUR-NPs)采用相同的方法制备,不添加卵磷脂和PEG-DSPE。设计并优化了LPNs体系中DTX和CUR的添加量和重量比,从大小和细胞Poison 性效率的角度出发。
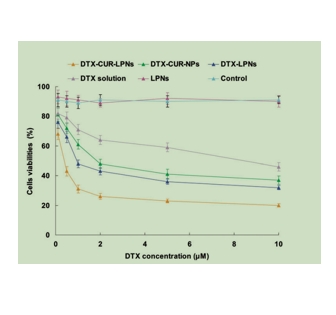
图为:lpn、NPs和游离药物的体外细胞有害性试验。
DTX是一种微管抑制剂,可导致有丝分裂阻滞在细胞周期的G2/M期,并最终导致细胞死亡。其临床应用受限于其MDR、高亲脂性和几乎不溶于水,以及DTX及其辅料产生的严重有害副作用。因此,迫切需要采取策略来提高其抗tumorTherapeutic effect 和减少其副作用。

 2024-12-17 作者:lkr 来源:
2024-12-17 作者:lkr 来源:

