文献:Highly biocompatible graphene quantum dots: green synthesis, toxicity comparison and fluorescence imaging
文献链接:https://xueshu.baidu.com/usercenter/paper/show?paperid=1y7600a05e320gm056040g80m4599027&site=xueshu_se&hitarticle=1
作者:Chaoren Yan, Xiaoling Hu, Ping Guan , Tongtong Hou , Peng Chen , Dewei Wan , Xinli Zhang , Jian Wang , and Chaoli Wang
相关产品:CGQDs
原文摘要:Graphene quantum dots (GQDs) have tremendous potential in biological imaging due to their bright visible photoluminescence mission. However, the tedious preparation procedures and potential toxicity of GQDs greatly limit their application in biological field. Here, highly biocompatible GQDs (HGQDs) have been successfully prepared only by glucose in aqueous solution. Compared with GQDs prepared from conventional methods (CGQDs), the cytotoxicity of HGQDs reduced by more than 60%, and the flow cytometric analysis of the normal cells treated with HGQDs showed that the early and late apoptotic rate reduced by more than 72% and 40%, respectively. In vitro fluorescence imaging showed that both cells and bacteria could be imaged by HGQDs, and the morphology of cells and bacteria could be kept to a maximum extent. A long-term in vivo study revealed that no obvious organ (heart, liver, spleen, lung and kidney) damage or lesions were observed, and the blood–brain barrier (BBB) could be overcome, which provides the possibility for treatment and diagnosis of brain-related diseases. With adequate studies of biocompatibility, both in vitro and in vivo, HGQDs may be considered for further biological application.
CGQD具有石墨烯的二维结构特征,但其尺寸效应使得其表现出量子性质。这些性质包括良好的光学性质(如荧光发射)、电学性质以及良好的水溶性等。此外,CGQD还易于进行表面修饰,如羧基化、胺基化等,从而进一步拓展其应用领域。CGQD在润滑领域具有潜在的应用价值。CGQD的独特润滑机制可以在甘油水溶液中形成坚固耐用的摩擦膜,从而触发自配钢触点的宏观超润滑。这种超润滑机制是通过石墨烯量子点在磨损金属表面的化学吸附,以及摩擦引起的结构降解和石墨烯量子点转变成层状石墨结构来实现的。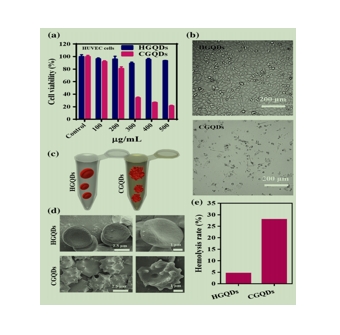
图为:用不同浓度的HGQDs和CGQDs处理的HUVEC细胞的细胞活力测定。
CGQDs在细胞活力测定中的应用:
将HUVEC和BH细胞接种到DMEM/HIGH葡萄糖和含有胎牛血清(FBS)的MEM Alpha培养基的微孔板中,在二氧化碳中孵育一段时间。然后将细胞在含有HGQDs和CGQDs的相同培养基溶液中培养。孵育一段时间后,用CCK-8法检测细胞活力。通过微孔板读数器测量形成的吸光度。
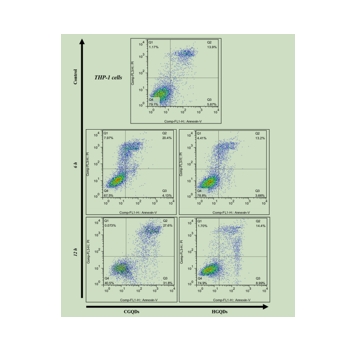
图为:HGQDs和CGQDs的Apoptosis 分析。
结论:通过CCK-8检测、流式细胞仪分析和共聚焦显微镜成像,通过对制备的体外细胞有害性和荧光成像研究,未发现急性有害性或形态学变化。HGQDs的生物相容性优于CGQD。离体植物的离体荧光成像器官显示HGQDs积聚静脉内注射HGQDs后无Inflammation。这些研究非常令人鼓舞,提供了大量的选择性和证据,GQDs在生物医学应用中的安全性。

 2024-12-18 作者:lkr 来源:
2024-12-18 作者:lkr 来源:

