文献:Synergistically Bifunctional Paramagnetic Separation Enables Efficient Isolation of Urine Extracellular Vesicles and Downstream Phosphoproteomic Analysis
文献链接:https://xueshu.baidu.com/usercenter/paper/show?paperid=18040my0ht2d0v50e34p0a80bs269423&site=xueshu_se
作者:Jie Sun, Shanying Han, Leyao Ma, Hao Zhang, Zhen Zhan, Hillary Andaluz Aguilar, Haiyang Zhang,Ke Xiao, Yanhong Gu, Zhongze Gu, and W. Andy Tao
相关产品:DSPE-PEG2000-COOH 磷脂-聚乙二醇2000-羧基
原文摘要:Extracellular vesicles (EVs) have emerged as important carriers for
intercellular communication and biological sources for diagnosis and therapeutics. Low efficiency in EV isolation from biofluids, however, severely restricts their downstream characterization and analysis. Here, we introduced a novel strategy for EV isolation from urine for prostate cancer diagnosis using bifunctionalized magnetic beads through high affinity Ti(IV)ions and the insertion of a phospholipid derivative, 1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine, into the EV membrane
synergistically. We demonstrated its efficient isolation of EVs from urine samples with low contamination, high recovery (>80%), and short separation time (within 1 h), resulting in the identification of 36,262 unique EV peptides corresponding to 3302 unique proteins and 3233 unique phosphopeptides representing 1098 unique phosphoproteins using only 100 μL and 5 mL urine samples, respectively. Coupled with trapped ion mobility spectrometry and parallel accumulation−serial
fragmentation for phosphositespecific resolution, quantitative phosphoproteomics of urine samples from prostate cancer patients and healthy individuals revealed 121 upregulated phosphoproteins in cancer patients in contrast to the healthy group. These particular advantages indicate that the novel bifunctional material enables sensitive EV phosphoproteomic analysis for noninvasive biomarker screening and early cancer diagnosis.
DSPE-PEG2000-COOH是由1,2-二硬脂酰-sn-甘油-3-磷酸乙醇胺(DSPE)、聚乙二醇(PEG)链(分子量约2000)和羧基(COOH)组成。DSPE部分具有良好的脂质双分子层亲和性,能使整个分子稳定地嵌入细胞膜结构中,为材料与生物膜的相互作用提供了基础。PEG2000链赋予了它良好的水溶性和生物相容性。而羧基(COOH)则为进一步的化学修饰提供了活性位点。可通过与含有氨基等活性基团的分子发生反应,如与化合物分子、靶向配体等连接,实现对化合物的靶向递送、提高化合物的稳定性和改善化合物的药代动力学特性,在化合物研发和生物领域有着应用前景。细胞外囊泡(EVs)已成为细胞间通信的重要载体。然而,从生物液体中分离的效率低,限制了其下游表征和分析。基于此该文献介绍了一种从尿液中分离EV,使用双功能化磁珠通过高亲和力Ti(IV)离子,并将磷脂衍生物协同插入到EV膜中。
图:基于BiMBs的EV分离和分析
BiMBs的制备和表征。
平行制备了三种磁珠,即仅用Ti(IV)固定的磁珠(TiMBs)、仅用DSPE-PEG2000-COOH(DspeMBs)和Ti(IV)和DSPE-PEG2000-COOH功能化的磁珠,BiMBs。首先制备了平均尺寸为400 nm的Fe3O4@SiO2磁珠。随后被胺基功能化,然后使用1-乙基-3-(3‘-二甲基氨基丙基)碳二亚胺(EDC)偶联和/或膦酸基引入DSPE-PEG2000-COOH分子来固定Ti(IV)离子。逐步监测了功能化磁珠的合成和表面分子性质。
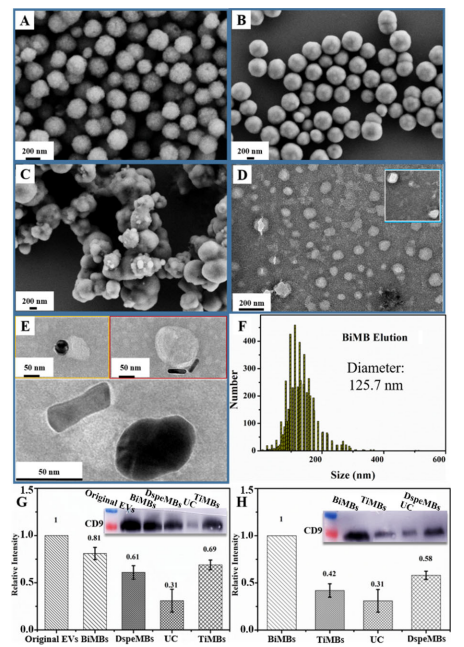
图:基于bimb的EV分离物的特性和验证。四氧化三铁磁珠的扫描电镜图像
结论:该文献探索了功能化磁性纳米材料(BiMBs,DspeMBs和TiMBs)隔离电动汽车从尿液基于疏水−疏水相互作用和金属离子之间的磷酸基和Ti(四)。这些功能化的磁珠用几种正交技术制备并进行了表征。通过对EV捕获效率、纯度、蛋白质组学和磷酸化蛋白质组学分析的评价,由于DSPE-PEG2000-COOH和Ti(IV)之间的协同效应,利用BiMBs和TIMS仪器对ev和样本进行无标记磷酸化蛋白质组学分析,鉴定了磷酸化过程中含有多个位置异构体的上调磷酸化蛋白。总的来说,BiMBs建立了一个方便的EV分离和下游蛋白质组学和磷酸化蛋白质组学分析的管道。

 2025-06-25 作者:ZJ 来源:
2025-06-25 作者:ZJ 来源:

