文献:Targeted Delivery of Chlorin e6 via Redox Sensitive Diselenide-Containing Micelles for Improved Photodynamic Therapy in Cluster of Differentiation 44-Overexpressing Breast Cancer
文献链接:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31057402/
作者:Chan Feng , Donglei Zhu , Lv Chen , Yonglin Lu , Jie Liu , Na Yoon Kim , Shujing Liang , Xia Zhang, Yun Lin, Yabin Ma and Chunyan Dong
相关产品:
Hyaluronic acid 透明质酸
原文摘要:The off-target activation of photosensitizers is one of the most well-known obstacles to effective photodynamic therapy (PDT). The selected activation of photosensitizers in cancer cells is highly desired to overcome this problem. We developed a strategy that enabled diselenide bonds to link hyaluronic acid (HA) and photosensitizer chlorin e6 (Ce6) to assemble the micelles (HA-sese-Ce6 NPs) that can target cancer and achieve a redox responsive release of drugs to enhance the PDT efficiency in breast cancer. The HA was used to form a hydrophilic shell that can target cluster of differentiation 44 (CD44) on the cancer cells. The selenium-containing core is easily dissembled in a redox environment to release Ce6. The triggered release of Ce6 in a redox condition and the positive feedback release by activated Ce6 were observed in vitro. In cytotoxicity assays and in vitro cellular uptake assays, the increased PDT efficiency and targeted internalization of HA-sese-Ce6 NPs in the cells were verified, compared to a free Ce6 treated group. Similar results were showed in the therapeutic study and in vivo fluorescence imaging in an orthotopic mammary fat pad tumor model. In addition, a significant inhibition of metastasis was found after the HA-sese-Ce6 NPs treatment. In general, this study promises an ingenious and easy strategy for improved PDT efficiency.
透明质酸(HA)是人体中的一种天然阴离子亲水性多糖,尤其在tumor基质中过表达。在许多上皮来源的 cancer 中,分化簇44(CD44)是 cancer 细胞表面主要上调的HA受体。HA可通过CD44调节 cancer 细胞的增殖和迁移。因此,HA作为一种很有前途的抗 cancer 药物靶向配体而受到了人们的关注。此外,HA具有高水溶性、良好的生物相容性、生物降解性和非免疫原性,并且很容易功能化。
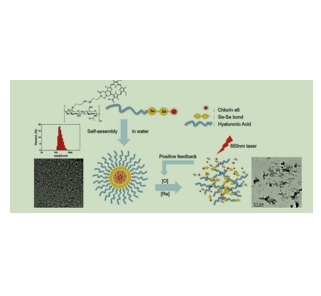
图为:自组装HA-sese-Ce6胶束、氧化还原敏感的Ce6释放和触发更多Ce6释放的正反馈回路的方案
HA-sese-NH2的合成:
将透明质酸(HA)与二盐酸硒代胱胺(或其他含二硒的化合物)按一定比例溶解在适当的溶剂中。在氨基-羧基反应条件下(如适当的pH值、温度和催化剂),使HA的羧基与二盐酸硒代胱胺的氨基发生反应,生成HA-sese-NH2。通过离心、透析等方法纯化产物,去除未反应的小分子和杂质。
HA-sese-Ce6的合成:
将Ce6溶解在适当的溶剂中,并调节其浓度。将HA-sese-NH2与Ce6按一定比例混合,并在氨基-羧基反应条件下使Ce6的羧基(或其他活性基团)与HA-sese-NH2的末端氨基发生反应,生成HA-sese-Ce6。同样通过离心、透析等方法纯化产物,去除未反应的小分子和杂质。
自组装形成胶束(HA-sese-Ce6 NPs):
将纯化后的HA-sese-Ce6溶解在去离子水中,通过自组装过程形成纳米胶束。利用磁力搅拌器使溶液充分混合,并在适当的温度下保持一段时间以确保自组装过程的完成。使用DLS等仪器测量胶束的粒径和分散性,以评估其稳定性和均一性。在HA-sese-Ce6 NPsTreatment 后,发现其对转移有抑制作用。
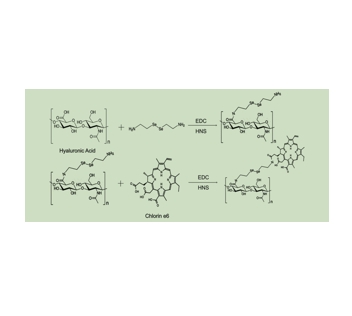
图为:Ce6的合成工艺
结论:通过上述实验步骤,可以成功合成出二硒化物键连接透明质酸HA和光敏剂Ce6的纳米胶束(HA-sese-Ce6 NPs)。该胶束具有良好的稳定性和均一性,并表现出对cancer细胞的靶向递送和氧化还原响应性释放的特性,为光动力疗法提供了新的药物递送系统。

 2024-12-18 作者:lkr 来源:
2024-12-18 作者:lkr 来源:

