文献:
Combined Photothermotherapy and Chemotherapy of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Guided by Multifunctional Nanomaterials Enhanced Photoacoustic Tomography
文献链接:
https://xueshu.baidu.com/usercenter/paper/show?paperid=1t0n06e025050ru0u55p0690jg639539&site=xueshu_se
作者:
Sujuan Zeng,Shiqi Liu,Yintao Lan, Ting Qiu, Mengyu Zhou, Weijian Gao,Wenyan Huang, Lihong Ge, Jian Zhang
相关产品:
DOX HA
原文摘要:Background: Squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck is the sixth most common cancer worldwide, with 40% occurring in the oral cavity. Although the level of early
diagnosis and treatment of OSCC has improved significantly, the five-year survival rate of advanced patients remains unsatisfactory. However, the main challenges before us are how to
get an early and accurate diagnosis and how to formulate effective treatment. Nanoparticlebased chemo-photothermal therapy has proven to be a promising non-invasive approach to treating oral squamous cell carcinoma treatment.
Methods: In this study, we tried to design and synthesize multifunctional hyaluronic acid
(HA) modified gold nanorods/mesoporous silica-based nanoparticles loaded with doxorubicin hydrochloride (DOX) for photoacoustic imaging (PAI) guided cooperative chemophotothermal therapy.
Results: The resultant nanocomposite shows favorable biocompatibility, relatively low cytotoxicity, ideal drug loading capability and strong PAI signals. In addition, they showed an excellent photothermal conversion efficiency of 49.02% for photothermal therapy (PTT).
Moreover, in vivo and in vitro experiments have shown that synergistic chemo-photothermal
therapy has better therapeutic effects than chemotherapy alone or PTT (P < 0.05). After being
injected into the CAL-27 tumor-bearing mice, the DOX-AuNRs@mSiO2-HA nanoparticles could accumulate rapidly at the tumor sites and achieve complete ablation of tumors when combined with near-infrared laser irradiation, without obvious side effects on normal tissues.
Conclusion: Our research provides a solid demonstration of the potential of DOX–AuNRs@mSiO2-HA as a multifunctional platform in PAI-guided photothermal chemotherapy for oral squamous cell carcinoma.
透明质酸(HA)是一种天然的、可生物降解的、非免疫原性聚合物,对CD44受体具有高亲和力,已被证明参与多种tumer包括tumer增殖、进展和转移的生物活性。HA壳包裹药物,发挥保护作用,增强药物的稳定性,实现药物的缓释。同时,将有效的抗tumer药盐酸阿霉素(DOX)通过静电相互作用即范德华力装入AuNRs@mSiO2的介孔二氧化硅中。HA分子通过酰胺键与AuNRs@mSiO2纳米颗粒偶联。综上所述,我们的DOX- AuNRs@mSiO2-HA纳米颗粒作为tumer靶向oral cancer。以下是制备过程:
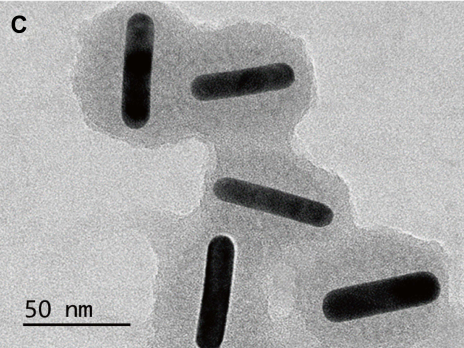
图:DOX-AuNRs@mSiO2-HA的TEM图像
纳米颗粒的合成
首先,用硼氢化钠化学还原HAuCl4,建立了CTAB帽封的Au种子。将CTAB与HAuCl4混合,加水固定体积。然后,在上述混合溶液中加入冰冷的硼氢化钠水溶液形成纳米金种子,然后,通过离心收集纳米颗粒。
AuNRs@mSiO2纳米粒子的合成
在上述获得的aunr中加入一定量的CTAB,在氢氧化钠溶液中调pH,将用甲醇稀释的TEOS试剂加入到业主的溶液中,最后收集获得
纳米粒子@msio2-nh2纳米粒子的合成
将3-氨基丙基三乙氧基硅烷(APTES)加入上述AuNRs@mSiO2乙醇溶液中,将AuNRs@mSiO2-NH2分散在20 mL硝酸铵乙醇溶液,回流过夜,离心洗涤2次。
DOX-AuNRs@mSiO2纳米粒子的合成
将DOX与AuNRs@mSiO2-NH2纳米颗粒混合,搅拌,离心后,得到DOX负载的AuNRs@mSiO2-NH2纳米颗粒。
DOX-AuNRs@mSiO2-HA纳米颗粒的合成
将HA分散在去离子水中,水合,然后将EDC和NHS混合,搅拌,激活HA的羧基。最后,在HA溶液中加入DOX-AuNRs@mSiO2,搅拌,离心洗涤后得到最终产物。
图:纳米金
结论:合成的纳米复合材料具有良好的生物相容性、相对良好的载药能力和较强的PAI信号。此外,光热疗法(PTT)的光热转换效率为49.02%。DOX-AuNRs@mSiO2-HA纳米颗粒注射到CAL-27小鼠体内后,联合近红外激光照射可在tumer部位快速积累,实现tumer完全消融,对正常组织无明显副作用。

 2024-12-18 作者:ZJ 来源:
2024-12-18 作者:ZJ 来源:

