文献:
Targeted delivery of antibiotics to the infected pulmonary tissues using ROS-responsive nanoparticles
文献链接:
https://jnanobiotechnology.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12951-019-0537-4作者:
Yu Wang, Qian Yuan, Wei Feng, Wendan Pu, Jun Ding, Hongjun Zhang, Xiaoyu Li, Bo Yang, Qing Dai, Lin Cheng, Jinyu Wang, Fengjun Sun and Dinglin Zhang
相关产品:
DSPE-PEG3400-FA(磷脂-聚乙二醇3400-叶酸)
原文摘要:
Background: Immunocompromised individuals and those with lung dysfunction readily acquire pulmonary bacterial infections, which may cause serious diseases and carry a heavy economic burden. Maintaining adequate antibiotic concentrations in the infected tissues is necessary to eradicate resident bacteria. To specifcally deliver therapeutics to the infected pulmonary tissues and enable controlled release of payloads at the infection site, a ROS-responsive material, i.e. 4-(hydroxymethyl) phenylboronic acid pinacol ester-modifed α-cyclodextrin (Oxi-αCD), was employed to encapsulate moxifoxacin (MXF), generating ROS-responsive MXF-containing nanoparticles (MXF/Oxi-αCD NPs).Results: MXF/Oxi-αCD NPs were coated with DSPE-PEG and DSPE-PEG-folic acid, facilitating penetration of the sputum secreted by the infected lung and enabling the active targeting of macrophages in the infammatory tissues. In vitro drug release experiments indicated that MXF release from Oxi-αCD NPs was accelerated in the presence of 0.5 mM H2O2. In vitro assay with Pseudomonas aeruginosa demonstrated that MXF/Oxi-αCD NPs exhibited higher antibacterial activity than MXF. In vitro cellular study also indicated that folic acid-modifed MXF/Oxi-αCD NPs could be efectively internalized by bacteria-infected macrophages, thereby signifcantly eradicating resident bacteria in macrophages compared to non-targeted MXF/Oxi-αCD NPs. In a mouse model of pulmonary P. aeruginosa infection, folic acid-modifed MXF/Oxi-αCD NPs showed better antibacterial efcacy than MXF and non-targeted MXF/Oxi-αCD NPs. Meanwhile, the survival time of mice was prolonged by treatment with targeting MXF/Oxi-αCD NPs.Conclusions: Our work provides a strategy to overcome the mucus barrier, control drug release, and improve the targeting capability of NPs for the treatment of pulmonary bacterial infections.
DSPE 是一种磷脂,其结构特点是含有亲水性的磷酸乙醇胺头部和两条疏水性的硬脂酰脂肪酸链。这种两性分子结构使其在生物膜的构建和稳定过程中发挥重要作用。PEG 是一种线性聚合物,具有良好的水溶性和生物相容性。分子量为 3400 的 PEG 在这个化合物中起到连接 DSPE 和叶酸(FA)的作用。同时,它可以增加整个分子的亲水性,防止纳米结构的聚集,并且减少非特异性蛋白吸附。叶酸是一种维生素,在细胞的许多生理过程中发挥重要作用。在这个化合物中,叶酸作为靶向配体。许多tumour细胞表面存在叶酸受体的高表达,该文献利用这一特性,将DSPE - PEG3400 - FA 通过叶酸与tumour细胞表面的叶酸受体特异性结合,从而实现对tumour细胞的靶向递送。基于DSPE-PEG3400-FA的相关特性,制备流程如下:
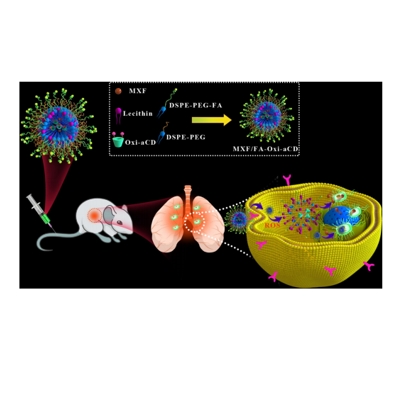
图:产品制备示意图及应用
制备了MXF/Oxi-αCD NPs:
将DSPE-PEG2000和卵磷脂分散在乙醇和去离子水中,然后在适宜温度下预热。同时,将MXF和 Oxi-αCD溶解在甲醇中,将所得溶液滴加入上述预热分散体中,涡旋。在适合温度下自组装,MXF/Oxi-αCD NPs在离心后,用F127洗涤,在超纯水中重悬。按照类似的步骤,制备了cy5标记的Oxi-αCD NPs和空白的Oxi-αCD NPs(不含MXF)。此外,fa修饰的MXF/Oxi-αCD NPs(简称MXF/FA-Oxi-αCD NPs)也用类似的方法制备,其中使用DSPE-PEG2000和 DSPE-PEG3400-FA。采用乳化液溶剂蒸发法制备cy5标记和空白PLGA NPs。在离心管放入MXF或Cy5染料,PLGA,溶解在二氯甲烷中,然后放聚乙烯醇,最后超声冰浴与探针超声器。将Te得到的乳液倒入的PVA中,在一定温度下搅拌。PLGA NPs)离心,用 F127洗涤几次,在超纯水中重悬。
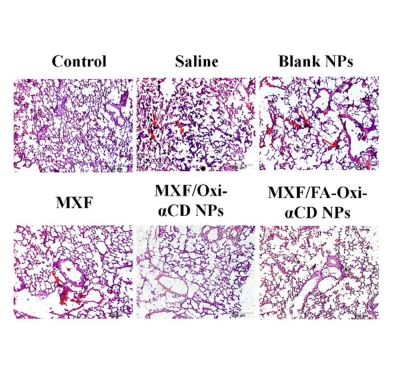
图:染色切片对照
结论:
该文献基于DSPE-PEG3400-FA成功制备出了被修饰的MXF/Oxi-αCD NPs,MXF/FA-Oxi-αCD NPs的主动靶向能力、黏液渗透能力和控制药物释放,增加了病理组织中的药物浓度,增强了体内的活性

 2024-12-18 作者: 来源:
2024-12-18 作者: 来源:

