文献:Construction and evaluation of red blood cells-based drug delivery system for chemo-photothermal therapy
文献链接:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0927776521002332
作者:Chen Wang , Jingru Huang , Yan Zhang, Hongxin Jia, Binbin Chen
相关产品:
DSPE-PEG3400-biotin 磷脂-聚乙二醇3400-生物素
原文摘要:In this study, a novel tumor-targeting drug delivery system (DDS) based on red blood cells (RBCs) were fabricated for combinational chemo-phototherapy against cancer. Cyclic peptide (cRGD) and indocyanine green (ICG) were applied to the surface of RBCs to increase the targeting and photothermal effect, respectively. Doxorubicin (DOX) as a model drug was loaded into RBCs by the hypotonic dialysis method. A series of tests have been carried out to evaluate the RBCs-based DDS and these tasks include physicochemical properties, cellular uptake, targeting
ability, and combination therapeutic efficiency. As a result, the DOX was successfully loaded into RBCs and the drug loading amount was 0.84 ± 0.09 mg/mL. There was no significant change of particle size after surface modification of RBCs. The RBCs-based DDS could target to the surface of cancer cells, which delivery DOX to the lesions efficiently and accurately. Meanwhile, due to the combined treatment effect, the RBCs-based DDS can effectively inhibit tumor growth. The RBCs-based DDS constructed in this research may have promising applications in cancer therapy due to their highly synergistic efficient therapy and to investigate its possibility for tumor therapy.
ICG-Biotin由吲哚菁绿和生物素通过化学反应结合而成,因此同时具有两者的性质。吲哚菁绿是一种近红外荧光染料,而生物素则具有生物亲和性,可以与亲和素或抗生物素结合,形成高亲和力的复合物。ICG-Biotin可以与生物大分子(如抗体、蛋白质、核酸)或细胞特异性配体结合,实现高度特异性的细胞标记和成像。红细胞化合物递送系统(DDS)作为一种新型的化合物输送平台,具有优势,如良好的生物相容性、长循环时间和低免疫原性等。该文献介绍了ICG-Biotin 作为一种具有特定功能的分子探针,在红细胞 DDS 特性分析中展现出了重要的应用价值。
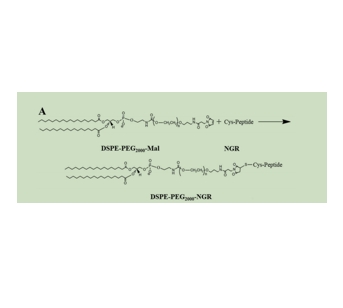
图为:基于红细胞的化合物传递系统示意图
ICG-Biotin在红细胞DDS特性分析中的应用:
将电子束撞击红细胞表面,并进行x射线分析,得到EDS分析光谱。与红细胞相比,红细胞生物素的硫、氮含量比(S/N)增加,说明生物素中的硫元素提高了S/ N值。同样,与rbc-生物素相比,R-RBC的S/N增加。这是由连接到红细胞表面的crgd-生物素引起的。将ICG-biotin修饰为红细胞后,R#I-RBC的S/N增加。红细胞在某处没有吸收峰,而ICG-Biotin和ICG-Biotin修饰的红细胞在某处有明显的吸收峰。ICG-Biotin修饰到红细胞表面的吸收强度低于ICG-生物素。这可能是生物素和亲和素之间的反应降低了ICG-Biotin的吸收强度。与ICG-Biotin相比,其他三组的发射波长呈蓝移趋势。蓝移的原因可能是荧光基团(ICG-生物素)与亲和素结合或与红细胞结合,改变了结构。它导致基态与激发态与第一激发态和基态之间的能级差发生变化。这些结果表明,已经成功地修饰了红细胞表面上的Biotin-ICG。以上实验结果证实了R#I-RBC的成功构建。
图为:R#I-RBC@DOX(B)的大小分布
结论:将 ICG-Biotin 与化合物或其他活性分子共同负载到红细胞中,通过检测红细胞内 ICG 的荧光强度,可以定量分析红细胞对化合物的负载效率。这有助于优化红细胞 DDS 的制备工艺,提高化合物负载量。利用 ICG 的近红外荧光特性,可以在动物体内进行荧光成像,跟踪红细胞 DDS 的体内分布情况。通过将生物素与特定的靶向分子结合,可以实现红细胞 DDS 的靶向输送。例如,将生物素与tumor细胞表面的特异性受体结合,使红细胞 DDS 能够靶向tumor组织,提高效果。

 2025-05-12 作者:lkr 来源:
2025-05-12 作者:lkr 来源:

