文献:
Microcosmic mechanisms for protein incomplete release and stability of various amphiphilic mPEG-PLA microspheres
文献链接:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22937802/
作者:
Yi Wei , Yu Xia Wang, Wei Wang, Sa V Ho, Feng Qi, Guang Hui Ma, Zhi Guo Su
相关产品:
原文摘要:
The microcosmic mechanisms of protein (recombinant human growth hormone, rhGH) incomplete release and stability from amphiphilic poly(monomethoxypolyethylene glycol-co-D,L-lactide) (mPEG-PLA, PELA) microspheres were investigated. PELA with different hydrophilicities (PELA-1, PELA-2, and PELA-3) based on various ratios of mPEG to PLA were employed to prepare microspheres exhibiting a narrow size distribution using a combined double emulsion and premix membrane emulsification method. The morphology, rhGH encapsulation efficiency, in vitro release profile, and rhGH stability of PELA microspheres during the release were characterized and compared in detail. It was found that increasing amounts of PLA enhanced the encapsulation efficiency of PELA microspheres but reduced both the release rate of rhGH and its stability. Contact angle, atomic force microscope (AFM), and quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation (QCM-D) techniques were first combined to elucidate the microcosmic mechanism of incomplete release by measuring the hydrophilicity of the PELA film and its interaction with rhGH.
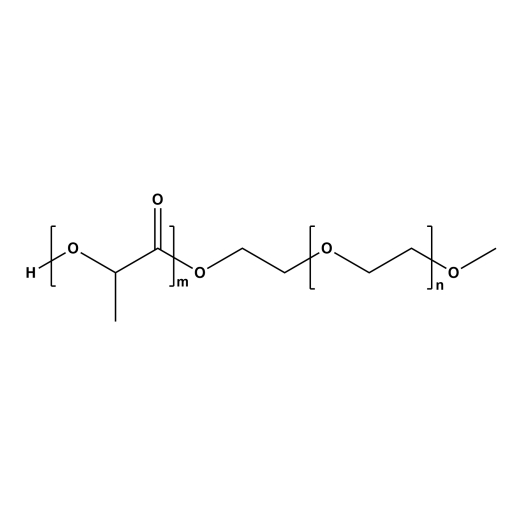
图为:甲氧基聚乙二醇-聚乳酸 PLA-MPEG结构式
本文献本研究两亲性聚(单甲氧基聚乙二醇 - co - D,L - 丙交酯)(mPEG - PLA,简称PELA)微球对rhGH的负载及释放特性,深入探究其不完全释放和稳定性的微观机制。mPEG具有良好的亲水性和生物相容性,而PLA则赋予材料一定的疏水性和可降解性,二者共聚形成的PELA材料兼具两者的优点,在药物缓释领域展现出应用潜力。
为了系统研究mPEG与PLA比例对PELA微球性能的影响,本文献设计了三种具有不同亲水性的PELA材料,分别命名为PELA - 1、PELA - 2和PELA - 3。这三种材料中mPEG与PLA的比例各不相同,使得它们在亲水性、降解速率等方面存在差异,为后续探究微球性能与材料组成之间的关系提供了样本。
在微球的制备过程中,本研究采用了双乳液和预混膜乳化相结合的创新方法。双乳液法能够有效地将rhGH包裹在微球内部,形成稳定的核 - 壳结构;而预混膜乳化技术则有助于控制微球的尺寸分布,制备出具有窄尺寸分布的微球。这种结合方法不仅提高了微球的制备效率,还保证了微球质量的均一性和稳定性,为后续的性能研究奠定了坚实的基础。
制备完成后,对PELA微球进行了全面而细致的表征。首先,通过扫描电子显微镜(SEM)观察微球的形态,发现所制备的微球呈规则的球形,表面光滑,无明显缺陷,且尺寸分布均匀,这表明所采用的制备方法能够有效地控制微球的形态和尺寸。接着,采用高效液相色谱法(HPLC)测定rhGH的包封率,结果显示,随着PLA用量的增加,PELA微球的包封效率提高。这是因为PLA的疏水性使得其与rhGH之间的相互作用增强,有利于将rhGH包裹在微球内部。
结论:选择具有足够PEG长度的合适亲水性聚合物对于制备蛋白质-药物缓释系统较为重要。在PELA微球中,mPEG链段的长度和比例直接影响着微球的亲水性、与rhGH的相互作用以及微球内部的微环境,进而影响rhGH的释放速率和稳定性。

 2025-05-16 作者:wff 来源:
2025-05-16 作者:wff 来源:

