文献:A hybrid 3D-printed aspirin-laden liposome composite scaffold for bone tissue engineering
文献链接:https://xueshu.baidu.com/usercenter/paper/show?paperid=163g0440911u04j0qe340m604r744408
作者:Yan Li, Yanjie Bai,Jijia Pan, Hui Wang,Hongming Li, Xiao Xu, Xiaoming Fu,Rui Shi,b Zuyuan Luo,Yongliang Li,Qian Li, Jerry Y. H. Fuhd and Shicheng Wei
相关产品:DSPE-PEG-NH2
原文摘要:Bone defects are some of the most difficult injuries to treat in clinical medicine. Evidence from cellular and animal studies suggests that aspirin exhibits protective effects on bone by promoting both the survival of osteoblast precursor stem cells and osteoblast differentiation. However, acquired resistance to aspirin and its cytotoxicity significantly limit its therapeutic application. Controlled release systems have been confirmed to promote the efficacy of certain drugs for bone regeneration. Additionally, the controlled release of a high dose of drug allows for lower dosing over an extended period. In this way, nano-liposomal encapsulation of
aspirin can be used to reduce the cytotoxicity of the overall dose. Using a series of osteogenic experiments, this study found that an aspirin-laden liposome delivery system (Asp@Lipo) obviously promoted osteogenesis and immunomodulation of human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs). We also studied the in vitro capacity of polycaprolactone (PCL)-based bioactive composite (PCL-Asp@Lipo) scaffolds to facilitate cell proliferation and osteoblast differentiation. Compared to a common scaffold, ALP assays, immunofluorescence and calcium mineralisation studies revealed that the PCL-Asp@Lipo scaffolds enhanced the osteogenic differentiation
of hMSCs. Subsequently, along with the cells, PCL and PCL-Asp@Lipo scaffolds were both implanted subcutaneously into nude mice for estimation of osteo-inductivity after 6 weeks, the PCL-Asp@Lipo composite scaffold exhibited more osteogenic activity than the bare PCL scaffold. This approach has potential applications in bone tissue repair and regenerative medicine.
脂质体被定义为磷脂囊泡,包括一个或多个同心的脂质双分子层,围绕着离散的水溶液,空间研究表明,脂质体可以为亲水性和亲脂性化合物提供良好的载化合物性,并提高化合物的溶解度和稳定性。脂质体通过稳定Treatment 性化合物促进了一系列生物医学应用,成为靶向化合物递送的纳米载体。阿司匹林通过促进成骨细胞前体干细胞的存活和成骨细胞的分化,对骨具有保护作用。然而,对阿司匹林的获得性耐化合物性限制了其Treatment 应用。研究发现,一种DSPE-PEG-NH2脂质体参与制备的富含阿司匹林的脂质体传递系统(Asp@Lipo)促进了人间充质干细胞(hMSCs)的成骨和免疫调节。研究基于聚己内酯(PCL)的生物活性复合材料(PCL-Asp@Lipo)支架促进细胞增殖和成骨细胞分化的体外能力。

图:含阿司匹林的脂质体复合支架示意图
采用薄膜分散法制备了富含阿司匹林的脂质体。将阿司匹林和DSPE-PEG-NH2脂质体溶解在甲醇和氯仿的混合物中,在一个圆底烧瓶中,并确定预定的比例用甲醇和氯仿混合物以不同的混合体积比制备阿司匹林。然后,使用旋转真空蒸发器除去甲醇和氯仿,脂质膜在磷酸盐缓冲盐水(PBS)中水合。在水浴超声后,得到含阿司匹林的脂质体。通过孔径分别为450、220和100 nm的多孔聚碳酸酯膜进行挤压,确保了最终脂质体的均匀性。然后用PBS透析含阿司匹林的脂质体。
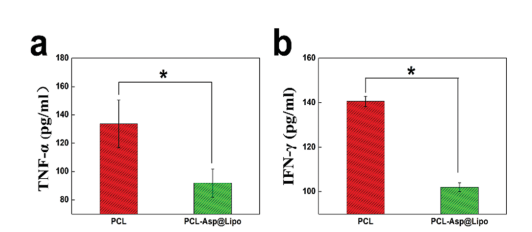
图:PCL-Asp@Lipo促进了皮下植入复合支架的免疫调节。与裸PCL组相比,PCL-Asp@Lipo降低了(a) TNF-a和(b) IFN-g的浓度
结论:与普通支架相比,ALP检测、免疫荧光和钙矿化研究显示,DSPE-PEG-NH2脂质体参与制备的PCL-Asp@Lipo支架增强了hMSCs的成骨分化。随后,将细胞、PCL和PCL-Asp@Lipo支架一起植入裸鼠皮下,以评估骨诱导性,PCL-Asp@Lipo复合支架比裸PCL支架表现出更多的成骨活性。具有拟议的化合物传递系统(Asp@Lipo)的生物活性支架可以作为促进骨诱导的仿生底物。

 2025-02-10 作者:ZJ 来源:
2025-02-10 作者:ZJ 来源:

