文献:The effect of size and surface ligands of iron oxide nanoparticles on blood compatibility
文献链接:https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/The-effect-of-size-and-surface-ligands-of-iron-on-Liu-Bai/b6db9fc2b07c01df3c67b105aececd7f66f6a3e6
作者:Tao Liu, Ru Bai, Huige Zhou, Rongqi Wang,Jing Liu, Yuliang Zhao and Chunying Chen
相关产品: Fe3O4@10PAA and Fe3O4@30PAA
原文摘要:Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) have been widely used and have attracted increased attention for their unique physicochemical properties, especially in biomedical sciences as contrast agents following intravenous administration. However, only few studies have systematically reported the blood compatibility of iron oxide nanoparticles with different physicochemical properties such as different sizes and surface ligands. Therefore, we selected three widely used organic ligands (polyacrylic acid, hyaluronic acid, and chitosan) with modified SPIONs at the same size of 5–6 nm, and polyacrylic acidmodified SPIONs with different sizes (5, 10, and 30 nm) at different concentrations to evaluate their haemocompatibility. Our results revealed that SPIONs modified with polyacrylic acid demonstrated sizedependent destruction of red blood cells and complement activation. Interestingly, 5 nm SPIONs prolonged blood clotting time as compared with 10 nm and 30 nm SPIONs in vitro. Compared with
polyacrylic acid-modified SPIONs, hyaluronic acid- and chitosan-modified SPIONs least affected red blood cells, platelets, coagulation, and complement activation. Hence, hyaluronic acid- and chitosancoated SPIONs are more suitable for nanomedicine applications than polyacrylic acid-coated SPIONs. Furthermore, the interaction between SPIONs and blood components strongly correlated with the administered concentration of nanoparticles. These results will provide some experimental information for safe-by-design SPIONs.
Fe3O4 内核赋予了 Fe3O4@10PAA磁性,使其能够在外部磁场的作用下实现快速定向移动和分离。PAA(聚丙烯酸)外壳为 Fe3O4 内核提供了保护,增强了材料的稳定性。它可以防止 Fe3O4 在空气中被氧化,同时也能提高材料在不同环境中的耐受性,使其能够在复杂的生理环境或化学体系中保持稳定的性能。Fe3O4@PAA 的表面可以进行多种化学修饰,以满足不同的应用需求。Fe3O4@10PAA 在生物体内表现良好的生物相容性,不会对生物体造成伤害。对于Fe3O4@10PAA和Fe3- O4@30PAA,本研究研究了不同尺寸(5、10、30)和表面配体(HA、CS、PAA)的影响。

图:不同铁浓度下SPIONs存在下红细胞的形态和聚集的扫描电镜图像。黄色箭头表示聚集的纳米颗粒。
使用了表面尺寸不同配体的四氧化三铁粒子,将其命名为Fe3O4@5PAA、Fe3O4@10PAA和Fe3O4@30PAA,另外两个命名为Fe3O4@HA和Fe3O4@CS。透射电镜结果显示,合成的三种纳米颗粒的平均尺寸为5-6nm,两种尺寸分别为10 nm和30nm(图1和B),且分散均匀。各颗粒的水动力尺寸表明,不同表面配体的SPIONs尺寸相似,各约为30 nm,而Fe3O4@10PAA和Fe3O4@30PAA的水动力直径分别为40 nm和60nm(图1C)。在SPIONs的FTIR光谱中(图。S2A),Fe3O4@nPAA显示出相似的峰,在约1710cm1处的峰值属于PAA的C]O拉伸振动。
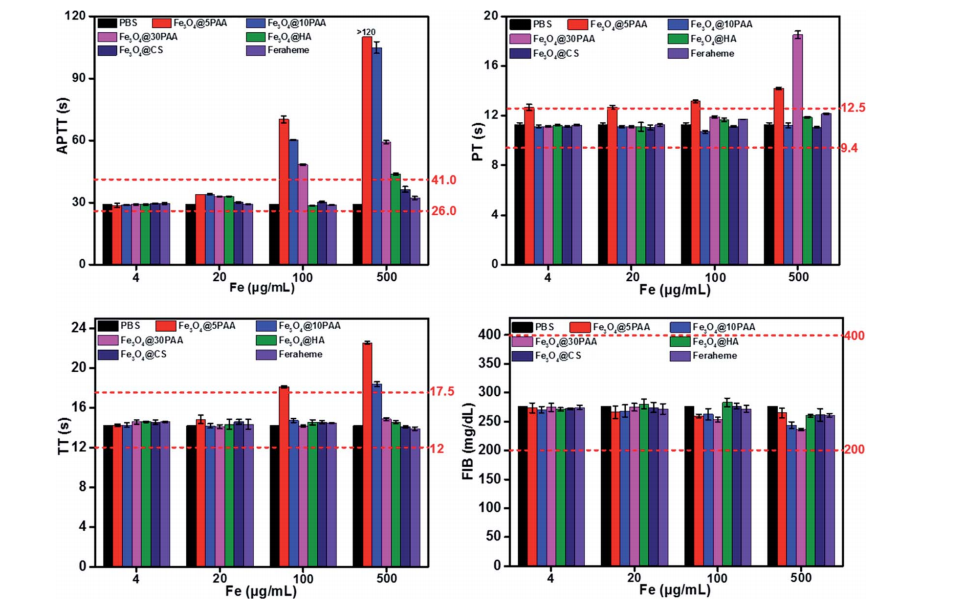
图:四种不同浓度SPIONs体外凝血试验结果。
结论:Fe3O4@5PAA、Fe3O4@10PAA和Fe3O4@30PAA三组对照组得出四氧化三铁Fe3O4纳米颗粒的尺寸对实验相容性的结果有影响。较小的粒径比较大的粒径具有更好的稳定性,相对较大直径在生理条件下不稳定,聚集迅速,对细胞有损伤。

 2025-02-10 作者:ZJ 来源:
2025-02-10 作者:ZJ 来源:

