文献:Triphenylphosphonium and D-α-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate-modified, tanshinone IIA-loaded lipid-polymeric nanocarriers for the targeted therapy of myocardial infarction
文献链接:https://xueshu.baidu.com/usercenter/paper/show?paperid=8870bd92f6550a515692536f49103681&site=xueshu_se
作者:Shouwen Zhang,Jingfang Li,Shunpeng Hu,Fangfang Wu,Xianzhao Zhang
原文摘要:Background: Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the leading causes of mortality worldwide. Currently, the best treatment options for myocardial infarction focus on the restoration of blood flow as soon as possible, which include reperfusion therapy, percutaneous coronary intervention, and therapeutic thrombolytic drugs. Materials and methods: In the present study, we report the development of lipid-polymeric nanocarriers (LPNs) for mitochondria-targeted delivery of tanshinone IIA (TN). D-α-tocopheryl polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate (TPGS) was linked to the triphenylphosphonium (TPP) cation. The LPNs were fabricated by nanoprecipitation method. LPNs were evaluated in vitro and in vivo in comparison with free drugs and other similar nanocarriers. Results: The mean diameter of TN/nanoparticles (NPs) was 89.6 nm, while that of TN/LPNs was 121.3 nm. The zeta potential of TN/NPs and TN/LPNs was −33.6 and −22.3 mV, respectively. Compared with free TN and TN/NPs, TN/LPNs exhibited significantly improved compatibility and therapeutic efficiency. In addition, the in vivo pharmacokinetics, biodistribution, and infarct therapy studies in Sprague Dawley rats showed that TPP-TPGS/TN/LPNs had better efficiency than their nonmodified TN/LPNs counterparts in all respects. Conclusion: These results indicated that the TPP-TPGS/TN/LPNs were promising nanocarriers for efficient delivery of cardiovascular drugs and other therapeutic agents for the treatment of CVDs.
FITC-PLGA(异硫氰酸荧光素-聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物)具有良好的生物可降解性,在体内可逐渐被分解代谢,减少对机体的长期不良影响。其次,异硫氰酸荧光素的标记使得材料具有荧光特性,便于在实验研究中进行可视化追踪,为研究化合物释放、细胞摄取等过程提供了有力工具。再者,PLGA 作为载体材料具有良好的生物相容性,降低免疫反应。它还可以通过调整 PLGA 的组成和分子量等参数来控制化合物释放速度,实现长效缓释。此外,FITC-PLGA 可加工成多种剂型,如纳米粒、微球等,满足不同的应用需求,在生物成像等领域具有应用前景。设计FITC-PLGA参与制备 TPP-TPGS/TN/LPNs,采用纳米共沉淀法制备了lpn。过程如下:
图:TPP-TPGS/TN/LPNs的结构方案图。
TPP-TPGS/TN/LPN的制备
采用纳米共沉淀法制备了TPP-TPGS/TN/LPNs。将TPP-Lys-TPGS和ISL分散在蒸馏水中形成水相。将TN、PLGA和聚山梨醇酯80溶解在丙酮中形成油相。在室温下轻轻搅拌,加入油相,直到有机溶剂完全蒸发,得到TPP-TPGS/TN/LPNs。采用TPP-TPGS修饰的空白LPNs(TPP-TPGS/LPNs),将PLGA(不含TN)溶解在丙酮中形成油相。
采用同样的方法制备非TPP-TPGS修饰的TN装载LPNs(TN/LPNs),将ISL(不含TPP-Lys-TPGS)分散形成LPNs)。非tpp-TPGS修饰的TN-负载聚合物NPs(TN/NPs)采用蒸馏法制备水(不含ISL和TPP-Lys-TPGS)作为水相。为了制备荧光标记的含FITC的LPNs和NPs,常规的PLGA被FITC-PLGA取代。通过超滤从悬浮液中分离lpn和NPs,去除游离化合物。
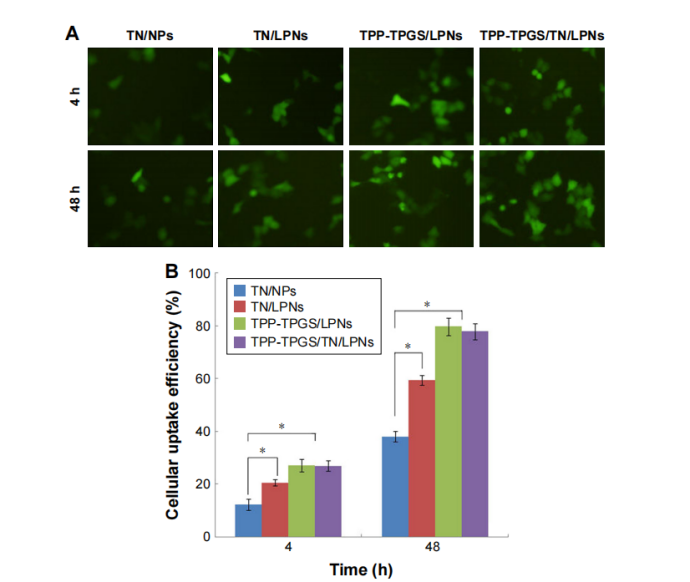
图:评估PC细胞对LPNs和NPs的细胞摄取,荧光强度
结论:合成了TPP-Lys-TPGS作为配体,并制备了TPP-TPGS/TN/LPNs作为一种化合物给化合物载体。与游离TN和TN/NPs相比,TN/LPNs表现出提高的相容性和Treatment 效率。此外,在SD大鼠体内的化合物代动力学、生物分布研究表明,TPP-TPGS/TN/LPNs在各方面的效率都优于未修饰的TN/LPNs。这些结果表明,TPP-TPGS/TN/LPNs是良好的纳米载体。

 2025-02-10 作者:ZJ 来源:
2025-02-10 作者:ZJ 来源:

