文献:Photoinduced PEG deshielding from ROS-sensitive linkage-bridged block copolymer
based nanocarriers for on-demand drug delivery
文献链接:https://www.cqvip.com/doc/journal/2714330632
作者:J Li,C Sun,W Tao,Z Cao,H Qian,X Yang,J Wang
相关产品:FITC-PLA 荧光素-聚乳酸
原文摘要:Controlling poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) shielding/deshielding at the desired site of action exhibits great advantages for nanocarrier-based on-demand drug delivery in vivo. However, the current PEG deshielding strategies were mainly designed for anticancer drug delivery;even so, their applications are also limited by tumor heterogeneity. As a proof-of-concept, we explored a photoinduced PEG deshielding nanocarrier TK-NPCe6&PTX to circumvent the aforementioned challenge. The TK-NPCe6&PTX encapsulating chlorin e6 (Ce6) and paclitaxel (PTX) was self-assembled from an innovative thioketal (TK) linkage bridged diblock copolymer of PEG with poly(d,L-lactic acid) (PEG-TK-PLA). We demonstrated that the high PEGylation of TK-NPCe6&PTX in blood helps the nanocarrier efficiently avoid rapid clearance and consequently prolongs its circulation time. At the desired site (tumor), 660-nm red light irradiation led to ROS generation in situ, which readily cleaved the TIC linkage, resulting in PEG deshielding. Such photo induced PEG deshielding at the desired site significantly enhances the cellular uptake of the nanocarriers, achieving on-demand drug delivery and superior therapeutic efficacy. More importantly, this strategy of photoinducing PEG deshielding of nanocarriers could potentially extend to a variety of therapeutic agents beyond anticancer drugs for on-demand delivery. (C) 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
该文献探讨了FITC标记聚乳酸(PLA)在基于光诱导聚乙二醇(PEG)去屏蔽的活性氧(ROS)敏感连接桥接块状共聚物纳米载体中的关键作用。该文献研究团队研究了一种新型的纳米载体,这种载体采用ROS敏感的连接桥来实现PEG的光诱导去屏蔽功能。具体来说,当纳米载体暴露于特定波长的光照射下,PEG链条会逐渐去除,从而释放出被包裹的化合物。这一过程能够根据tumour微环境中的ROS水平和外部光照的变化,实现对化合物释放的准确控制。其中FITC标记的PLA发挥了重要作用。首先,FITC作为荧光标记物,使研究人员能够实时监测纳米载体在体内的分布及其化合物释放的过程。通过荧光成像技术,研究人员观察到随着光照时间的延长,PEG链条的去除程度与PLA的释放速率呈正相关,这为化合物释放机制提供了直接的证据。
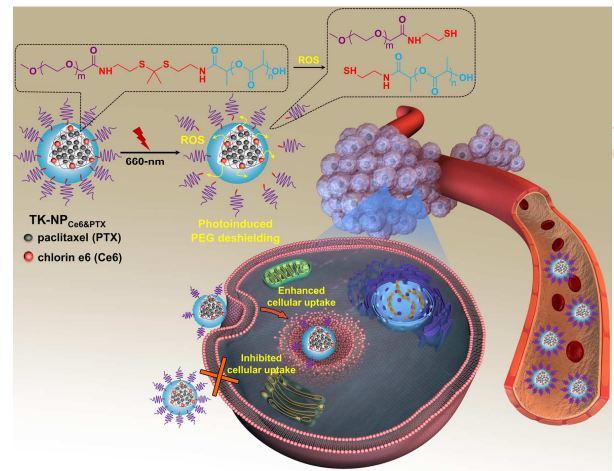
图为:ros敏感的链桥联二嵌段共聚物基纳米载体TK-NPCe6和PTX用于光诱导PEG去除按需给药的示意图。
TK-NPCe6&PTX和NPCe6&PTX的制备:为制备TK-NPCe6和PTX,将Ce6、PTX和mPEG113-TK-PLA14010溶于二甲亚砜中,然后滴加入水,连续搅拌。然后,将混合物溶液转移到透析管中,以去除DMSO。最终溶液通过0过滤器(密理孔)过滤。NPCe6和PTX的制备方法类似,用mPEG113-b-PLA142取代mPEG113-TK-PLA140。同样,在此过程中加入FITC标记的PLA制备了FITC标记的纳米载体FITCTK-NPCe6和PTX和FITCNPCe6和PTX。
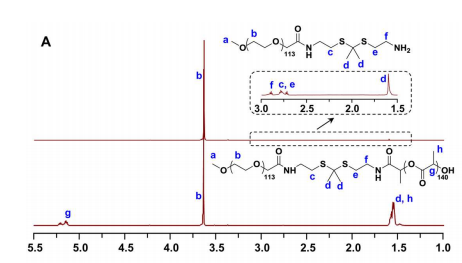
图为:mPEG113-TK和mPEG113-TK-PLA140的1H NMR谱。
结论:研究表明,FITC-labeled PLA作为荧光标签,能够有效地跟踪纳米载体在细胞内的分布和释放过程。结合光诱导的PEG去掩蔽机制,PLA的引入增强了化合物的靶向性和释放的可控性。该系统利用活性氧(ROS)敏感的连接桥,使得在特定条件下,化合物能够迅速释放,从而提具有效率率。此外,FITC标记的PLA也有助于评估纳米载体的细胞摄取和化合物释放的时效性,为实现智能化的按需化合物释放提供了可视化支持。

 2025-06-13 作者:wff 来源:
2025-06-13 作者:wff 来源:

