文献:Proximity-constructed bifunctional DNA probes for identification of stem-like biomarker in breast cancer
文献链接:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0925400520313915
作者:Ying Wang, Langjian Dong , Jing Zhao , Mohammed Jalalahc, M.S. Al-Assirib , Farid A.Harrazb , Ya Cao
相关产品:Azide-biotin 叠氮-生物素
原文摘要:CD44, a stem-like biomarker, plays a critical role in maintenance of stem-like phenotype in breast cancer and is associated with migration, invasion and apoptosis resistance of breast tumors. Herein, we designed an effective sensing method using proximity-constructed bifunctional DNA probes for electrochemical identification of CD44. In our design, hybridization of capture probes was stabilized by target CD44 binding-induced proximity, thereby initiating subsequent cyclic strand displacement reactions. As a result, signaling probes were produced and dual-labeled with dibenzocyclooctyne group and CdTe quantum dots (QDs). These signaling probes performed two functions, specifically enrichment on azide-functionalized magnetic beads via click chemistry and generation of amplified electrochemical signaling relied on QDs. With aid of these bifunctional probes, the sensing method allowed not only highly specific identification of target CD44 even in serum samples and breast cancer cells but also monitoring of CD44 expression changes upon siRNA treatment. The linear range for CD44 identification was 0.1 to 1000 ng/mL and the detection limit was 0.0792 ng/mL, which displayed an improved sensitivity compared to previous reports. Therefore, the method may provide a powerful tool for CD44 identification and have a great potential in revealing stem-like properties in breast cancer in the future.
Azide-biotin 分子中同时包含生物素基团和叠氮基团。生物素是生物体内多种羧化酶的辅基,能与生物素结合蛋白或抗体等具有高度特异性的结合;叠氮基作为一种活泼的官能团,可参与多种化学反应。这种结构使得 Azide-biotin 既能够利用生物素的特性与生物分子进行特异性结合,又能借助叠氮基的反应活性,通过点击化学反应与含有炔烃的分子形成稳定的三唑键,从而实现对生物分子的标记和追踪等功能。CD44是一种茎样生物标志物,在维持 breast
cancer茎样表型中起作用,并与breast tumor的迁移、侵袭和Apoptosis 抵抗有关。基于介绍一种传感方法,利用接近构建的双功能DNA探针对CD44进行电化学鉴定。叠氮化物的制备和捕获探针的获得过程如下:
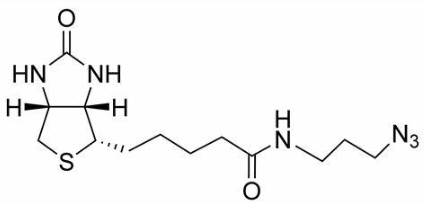
图:Azide-biotin 结构式
叠氮化物的制备和捕获探针
为了制备叠氮化物@MBs,首先用PBS洗涤链霉亲和素功能化磁珠。然后,将磁珠重新悬浮在叠氮化物生物素的PBS中,室温孵育。然后,通过磁分离纯化叠氮化物@MBs,并在PBS中重新悬浮以供进一步使用。为制备捕获探针,将 CD44抗体(Ab1或Ab2)和 Sulfo-SMCC混合在PBS中,室温孵育。然后,将混合物转移到超滤离心管(MWCO 30 K)中,离心。将上部未过滤的物质重新溶解于PBS中,加入DNA探针(DNA1或DNA2),反应。然后,用超滤离心管再次离心,将上部未过滤的捕获探针(DNA1-Ab1或DNA2- Ab2)收集于 PBS中进一步使用。
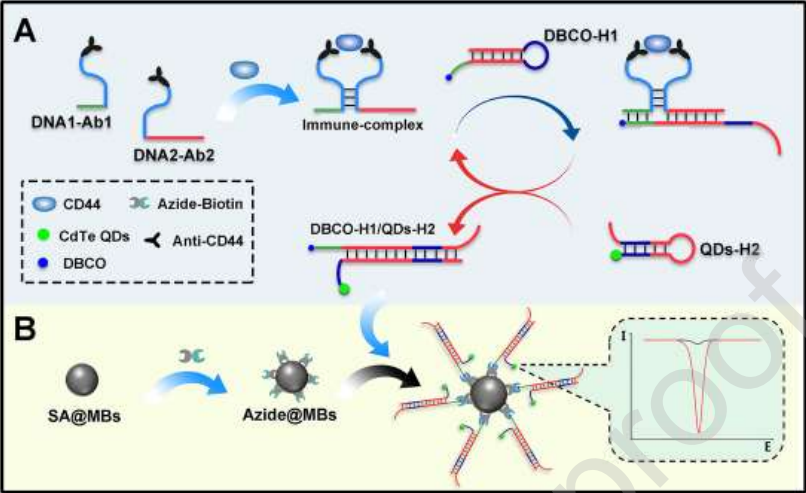
图:用于鉴定茎样生物标志物CD44的邻近构建的双功能DNA探针示意图
结论:构建的双功能DNA探针的breast cancer茎状生物标志物。一对捕获探针能够利用抗体部分选择性地同时结合靶标蛋白,靶标结合诱导的接近随后稳定了DNA部分的杂交。然后,启动循环DNA组装,生成增加的双标记DNA双工,满足了电化学检测中信号富集和“信号通”输出的要求。以H2为模板制备的QDs-H2能够释放大量金属离子,增强电化学信号。该方法也被用于监测sirna转染的CD44阳性 breast cancer细胞中CD44表达的下调。该方法在细胞样本中表现出了灵敏度、特异性和可用性。

 2025-02-11 作者:ZJ 来源:
2025-02-11 作者:ZJ 来源:

