文献:Effects of Platycodins Folium on Depression in Mice Based on a UPLC-Q/TOF-MS Serum Assay and Hippocampus Metabolomics
文献链接:https://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/24/9/1712
作者:Cuizhu Wang , Hongqiang Lin , Na Yang , Han Wang , Yan Zhao , Pingya Li ,Jinping Liu , Fang Wang
相关产品:19 (S)-HETE 19(S)-羟基二十碳四烯酸
原文摘要:Major depressive disorder (MDD), also known as depression, is a state characterized by low mood and aversion to activity. Platycodins Folium (PF) is the dried leaf of Platycodon grandiflorum,with anti-inflammatory and antioxidative activities. Our previous research suggested that PF wasrich in flavonoids, phenols, organic acids, triterpenoid saponins, coumarins and terpenoids. This study aimed to investigate the antidepressant effect of PF using lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced depressive mice. Several behavior tests (sucrose preference test (SPT), forced swimming test (FST) and tail suspension test (TST)) and biochemical parameters (IL-6, TNF-α and SOD levels) were used to evaluate the antidepressive effect of PF on LPS-induced depression model. Furthermore, a UPLC-Q/TOF-MS-based metabolomics approach was applied to explore the latent mechanism of PF in attenuating depression. As a result, a total of 21 and 11 metabolites that potentially contribute to MDD progress and PF treatment were identified in serum and hippocampus, respectively. The analysis of metabolic pathways revealed that lipid metabolism, amino acid metabolism, energy metabolism,arachidonic acid metabolism, glutathione metabolism and inositol phosphate metabolism were disturbed in a model of mice undergoing MDD and PF treatment. These results help us to understand the pathogenesis of depression in depth, and to discover targets for clinical diagnosis and treatment.They also provide the possibility of developing PF into an anti-depressantive agent.
谷胱甘肽(GSH)可以防止一些含硫醇的蛋白质或酶被一些氧化剂如过氧化物损伤。桔梗(PF)是桔梗干叶,具有抗炎和抗氧化活性,PF富含黄酮类、酚类、有机酸、三萜皂苷、香豆素和萜类。探讨脂多糖(LPS)诱导的小鼠的抗depressed作用。采用行为试验(蔗糖偏好试验(SPT)、强迫游泳试验(FST)和尾悬试验(TST))和生化指标(IL-6、TNF-α和SOD水平)评价PF对脂多糖诱导depressed模型的抗depressed作用。此外,采用基于UPLC-Q/TOF-ms的代谢组学方法来探讨PF减轻depressed的潜在机制。
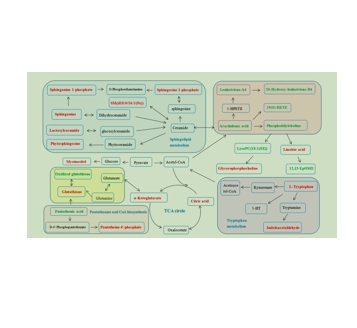
图为:血清和海马的代谢途径
脂多糖诱导的depressed模型被用于评价抗depressed药物的活性。体重、蔗糖偏好、强迫游泳试验(FST)和尾悬吊试验(TST)的活动时间以及IL-6、TNF-α和SOD水平是常用的指标。基于UPLC-Q/TOF-MS的代谢组学研究结合多变量统计分析进一步说明了PF的抗depressed作用。首先,PCA分析发现正常对照组、LPS诱导的模型组和HPF组(位于正常组和模型组之间,倾向于正常组)明显分离,发现LPS诱导的代谢紊乱明显受到PF处理的调节。其次,在研究中发现了潜在的生物标志物,这清楚地表明PF可以调节甘油磷脂代谢、色氨酸代谢、鞘脂代谢、花生四烯酸代谢、亚油酸代谢、谷胱甘肽代谢、TCA循环、泛酸和辅酶a生物合成以及肌醇磷酸代谢的改变。
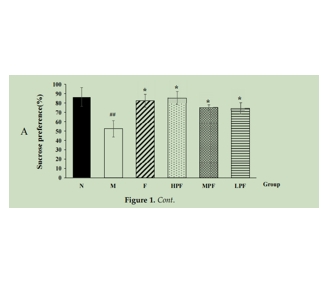
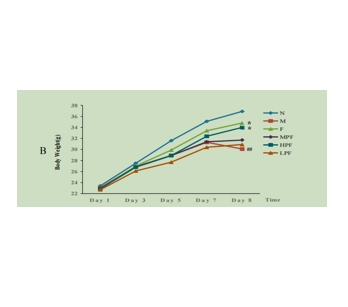
图为:PF对SPT (A)和BW (B)的影响
结果,PF干预可增加蔗糖偏好和体重,减少静止时间,降低细胞因子TNF-α和IL-6水平,提高SOD水平。行为和生化结果显示,PF的行为调节作用伴随着PF诱导的血清IL-6和TNF-α水平和海马SOD水平的调节。PF的抗depressed作用与抗炎活性和抗氧化活性有关。在血清和海马中分别鉴定出可能有助于MDD进展和PFTreatment 的代谢物。代谢途径分析显示,在接受MDD和PFTreatment 的小鼠模型中,脂质代谢、氨基酸代谢、能量代谢、花生四烯酸代谢、谷胱甘肽代谢和肌醇磷酸盐代谢受到干扰。

 2025-02-11 作者:lkr 来源:
2025-02-11 作者:lkr 来源:

