文献:Temporary suppression the sequestrated function of host macrophages for better nanoparticles tumor delivery
文献链接:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29869519/
作者:Jifu Hao , Te Han , Meixiang Wang, Qiannan Zhuang , Xiaodan Wang, Jianguo Liu , Yongan Wangand Hua Tang
相关产品: Phosphatidylcholine cholesterol
原文摘要:Orchestration of nanoparticles to achieve targeting has become the mainstream for efficient delivery of antitumor drugs. However, the low delivery efficiency becomes the biggest barrier for clinical translation of cancer nanomedicines, as most of them are sequestrated in the liver where more macrophages located in are responsible for capture of systemic administrated nanoparticles. In this study, we found that the depletion of the liver macrophages could lead to a superior improvement in the nanoparticles delivery. Firstly, we developed clodronate-containing liposomes (clodrolip) to transiently suppress the phagocytic function of macrophages, the residual macrophages in liver only accounted for less than 1% when the mice were treated with clodrolip in advance. In addition, the pharmacokinetics results of treatment with
paclitaxel-poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PTX-PLGA) nanoparticles disclosed that the AUC of PTX in the macrophages depletion group increased 2.11-fold. These results meant that the removal
of macrophages would decrease the nanoparticles accumulation in the liver and better the biodistribution and bioavailability of nanoparticles delivery systems. Moreover, treatment of mice with melanoma by the combination of clodrolip and PTX-PLGA nanoparticles resulted in an elevated anti-tumor efficacy, the tumor inhibition ratio was nearly reached to 80%. Furthermore, these combinatorial regimens have demonstrated negligible toxicity in incidence of adverse effects. In conclusion, the encouraging results from this study inspire the generation of a rational strategy to focus on microenvironmental priming for modulation of innate immunity and to improve delivery efficiency of nanoparticles.
胆固醇是一种白色的结晶物质脂质分子。它是细胞膜的组成部分,能够维持细胞膜的稳定性和流动性。同时,它也是合成胆汁酸、维生素 D 以及多种激素的前体物质。卵磷脂是一种浅黄色至棕色的粉末或颗粒状营养物质。卵磷脂富含磷脂酰胆碱、磷脂酰乙醇胺等成分,具有多种生理功能。它是细胞膜的重要组成部分,有助于维持细胞的正常结构和功能。同时,卵磷脂在人体代谢中起着作用,能够促进脂肪的代谢和转运,防止脂肪在肝脏等部位的积聚。基于此开发含氯膦酸盐的脂质体以关注微环境启动来调节先天免疫和提高纳米颗粒的递送效率。
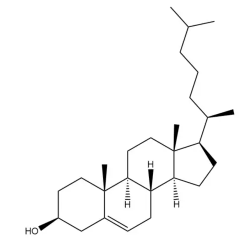
图:胆固醇结构式
氯膦酸脂质体的制备
将磷脂酰胆碱和胆固醇共溶在一个圆底烧瓶中的氯仿中。通过旋转蒸发完全去除氯仿并在烧瓶内部形成薄膜后,用氯膦酸盐的PBS水合形成的脂质膜。然后,对获得的悬液进行探针超声检查。离心后,去除过多的氯膦酸盐,用PBS冲洗获得的氯膦酸盐脂质体。随后,用PBS重悬丁香瓣以供进一步使用。
图:脂质体
结论:通过磷脂酰胆碱和胆固醇制备的氯膦酸盐脂质体用于巨噬细胞预处理方法来改善纳米颗粒的tumor递送。可以有效地消耗肝脏中的巨噬细胞;这些细胞可以隔离最多的循环纳米颗粒。巨噬细胞能更好地提高纳米颗粒的生物分布和输送系统的性能。此外,与其他组相比,联合使用PTX-PLGA纳米颗粒对巨噬细胞预处理也产生了作用。

 2025-02-12 作者:ZJ 来源:
2025-02-12 作者:ZJ 来源:

