文献:In vitro and in vivo antitumor effects of lupeol-loaded galactosylated liposomes
文献链接:
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/10717544.2021.1905749
作者:Jun Zhang , Xixi Hu , Guohua Zheng , Hui Yao , Huali Liang
相关产品:Galactose-PEG-DSPE(半乳糖-聚乙二醇-磷脂)
原文摘要:
Lupeol liposomes, modified with Gal-PEG-DSPE, were developed following a thin-film dispersion method. Then, the morphology, physicochemical properties, and in vitro release properties of those liposomes were investigated. The scanning electron microscopic images showed that most of the liposomes were spherical particles; they were similar in size and uniformly dispersed. Both lupeol liposomes and Gal-lupeol liposomes exhibited an average particle size of about 100 nm. The encapsulation efficiency was greater than 85%. The encapsulation efficiency of lupeol liposome and Gal-lupeol liposome, stored with 15% sucrose as glycoprotein for 6 months, was higher than 80%; although the particle size increased, they remained within 200 nm. The cell-uptake study demonstrated that the Gal-lupeol-liposome uptake efficiency was the highest in HepG2 cells. The HepG2 cells treated with the Gal-lupeol liposomes had higher apoptotic efficiency than the lupeol liposome and free lupeol. After HepG2 cells were treated with Gal-lupeol liposome, the expressions of AKT/mTOR-related proteins (p-AKT308 and p-AKT473) were also significantly reduced than the lupeol-liposome and free lupeol group. The in vivo targeting studies showed that Gal-NR-L exhibited liver-targeting effects on FVB mice. The pharmacodynamic study was performed by transfecting AKT and c-MET via the high-pressure tail vein of FVB mice. After Gal-lupeol-L administration, the liver index and liver weight of mice were less than those non-targeted group. The histopathological study showed that the lobular structure in the mice liver was clearer, the vacuoles were more obvious, and the cytoplasm was more abundant after Gal-lupeol-L administration. Also, the qRT-PCR study showed that AFP, GPC3, and EpCAM mRNA expression levels were significantly lower than those non-targeted lupeol-liposomes.
Galactose-PEG-DSPE:Galactose - PEG - DSPE 是一种多功能的化合物,主要由半乳糖(Galactose)、聚乙二醇(PEG)和 1,2 -二硬脂酰-磷脂酰乙醇胺(DSPE)组成。半乳糖是一种单糖,在生物体内存在,尤其在糖类代谢和细胞识别过程中发挥作用。PEG 是一种具有良好水溶性和生物相容性的聚合物,它可以改善化合物的溶解性和稳定性。DSPE 是一种磷脂,是生物膜的重要组成成分,其亲脂性有助于与细胞膜相互作用。在 Galactose - PEG - DSPE 结构中,半乳糖通常通过化学键连接到聚乙二醇(PEG)的一端,而 DSPE 连接在 PEG 的另一端。这种结构设计使得化合物同时具备亲水性(由半乳糖和 PEG 提供)和亲脂性(由 DSPE 提供)的特性,有利于在不同的生物环境中发挥作用。基于Galactose - PEG - DSPE的性能,lupeol负载Galactose-PEG-DSPE脂质体合成如下:
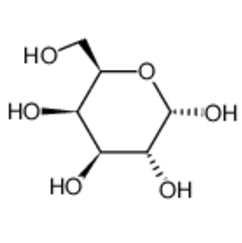
图:Galactose结构式
lupeol负载Galactose-PEG-DSPE脂质体的制备:
将lupeol,HSPC,胆固醇和Galactose-PEG-DSPE以一定的摩尔比溶解在甲醇/氯仿的溶剂中。使用旋转真空蒸发器将有机溶剂蒸发至干燥,并用磷酸盐缓冲盐水(PBS) 水化一段时间。脂质悬浮液经超声细胞破碎机超声处理。最后,将脂质体悬浮液通过微孔过滤器过滤,去除游离的 lupeol。Lupeol 脂质体(Lupeol - L)的制备方法类似,只是去除了Galactose-PEG-DSPE。
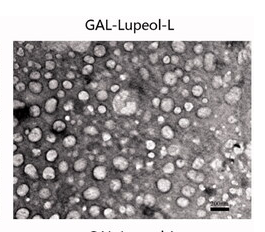
图:脂质体表征
结论:
该文献成功制备出基于Galactose - PEG - DSPE合成lupeol负载Galactose-PEG-DSPE脂质体。数据表明,Gal-lupeol-L表现出良好性能:大小相似,分布均匀,包封率高,摄取率好,还具有更高的Apoptosis 效率。

 2025-07-24 作者:ws 来源:
2025-07-24 作者:ws 来源:

