文献:Curcumin–polydopamine nanoparticles alleviate ferroptosis by iron chelation and inhibition of oxidative stress damage
文献链接:https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlehtml/2024/ra/d4ra02336f
作者:Li Lei , Jiali Yuan , Qingqing Yang , Qiuxia Tu , Haijun Yu , Liangzhao Chu , Lei Tang , Chunlin Zhang
相关产品:Fmoc-PEG-MAL(9 -芴甲氧羰基-聚乙二醇-马来酰亚胺)
原文摘要:
Ferroptosis, characterized by elevated iron levels and lipid peroxidation (LPO), is a recently identified regulatory mechanism of cell death. Its substantial involvement in ischemic tissue injury, neurodegenerative disorders, and cancer positions ferroptosis inhibition as a promising strategy for managing these diverse diseases. In this study, we introduce curcumin–polydopamine nanoparticles (Cur–PDA NPs) as an innovative ferroptosis inhibitor. Cur–PDA NPs demonstrate remarkable efficacy in chelating both Fe2+ and Fe3+ in vitro along with scavenging free radicals. Cur–PDA NPs were found to efficiently mitigate reactive oxygen species, reduce Fe2+ accumulation, suppress LPO, and rejuvenate mitochondrial function in PC12 cells. Thus, these NPs can act as potent therapeutic agents against ferroptosis, primarily via iron chelation and reduction of oxidative stress.
Fmoc-PEG-MAL:Fmoc - PEG - MAL 是一种含有多个活性官能团的化合物。其中 “Fmoc” 是 9 - 芴甲氧羰基(9 - Fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl),它是一种常用的氨基保护基团;“PEG” 是聚乙二醇(Polyethylene glycol),具有良好的水溶性和生物相容性;“MAL” 是马来酰亚胺(Maleimide),是一种能够与巯基(- SH)特异性反应的活性官能团。这种化合物的结构特点是通过聚乙二醇链将芴甲氧羰基和马来酰亚胺基团连接起来。聚乙二醇链的长度可以根据合成需求而变化,其分子量大小会影响化合物的物理化学性质,如溶解性、流动性等。基于Fmoc-PEG-MAL的相关性能,纳米粒子Cur-PDA NPs的合成如下:
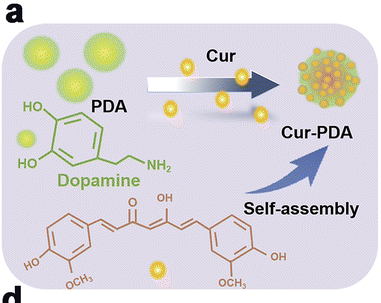
图:合成示意
Cur-PDA NPs的制备:
将NH4OH、乙醇和去离子水混合,加入圆底烧瓶中。室温搅拌,取DA溶于去离子水中,加入上述混合物,调节pH 。然后,将 Cur 和Fmoc-PEG-MAL 溶解在DMSO中,并加入上述混合物中。在遮光条件下搅拌,离心收集沉淀,用DMSO/水的混合物洗涤,干燥备用。采用紫外可见光谱法测定Cur的负载效率(LE)和包封效率(EE)。
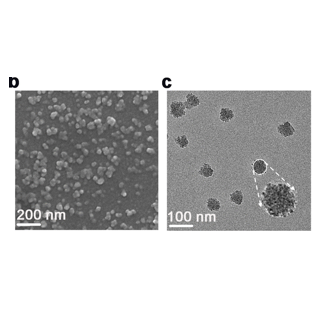
图:表征示意
结论:
该文献成功制备出基于Fmoc-PEG-MAL合成的纳米粒子Cur-PDA NPs。研究发现,Cur-PDA NPs 在体外螯合 Fe 2+和 Fe 3+以及清除自由基方面表现出明显的功效,可以有效地减轻PC12细胞中的活性氧、减少Fe 2+积累、抑制LPO并恢复线粒体功能。因此,纳米粒子Cur-PDA NPs可以通过铁螯合和减少氧化应激作为抗铁dead的有效heal剂。

 2025-08-05 作者:ws 来源:
2025-08-05 作者:ws 来源:

