文献:Pharmacokinetics of a liposomal formulation of doxorubicin in rats
文献链接:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28579888/
作者:Zongyu Liu , Ye Bi , Yating Sun , Fei Hao , Jiahui Lu , Qingfan Meng , Robert J. Lee , Yaping Tian ,Jing Xie
相关产品:DSPE-PEG2000(二硬脂酰基磷脂酰乙醇胺-聚乙二醇)
原文摘要:
Measuring free drug concentration following systemic administration of a liposomal drug is a crucial aspect of the assessment of its in vivo behavior. Therefore we require an efficient method to separate free drug in the plasma from encapsulated drug. Objectives: To study the pharmacokinetics of freedoxorubicin (DOX) released from liposomal doxorubicin (L-DOX) in rats. Methods: L-DOX was prepared with encapsulation efficiency of 90% and was injected intravenously into rats. A solid-phase extraction (SPE) method coupled with UPLC–MS/MS was used to measure the concentration of F-DOX in rat plasma without disrupting the integrity of L-DOX. Results: This method exhibited a linear range of F-DOX from 0.2 to 200 ng/mL. Recovery, precision, linearity and accuracy of this technique appear satisfactory for pharmacokinetic study. The constituents of F-DOX ranged from 5.35% to 14.09% of total DOX in plasma at each time point measured after L-DOX administration. Conclusion: SPE method was suitable for studying the pharmacokinetics of F-DOX in rats receiving L-DOX.
DSPE-PEG2000由磷脂酰乙醇胺(DSPE)和聚乙二醇(PEG,分子量为2000)通过化学共价结合而成。DSPE-PEG2000结合了PEG的水溶性和生物相容性,以及DSPE的细胞膜亲和性,使其成为一种纳米载体。通过将其与化合物结合,可以实现靶向传递,提高效果并减少副作用。
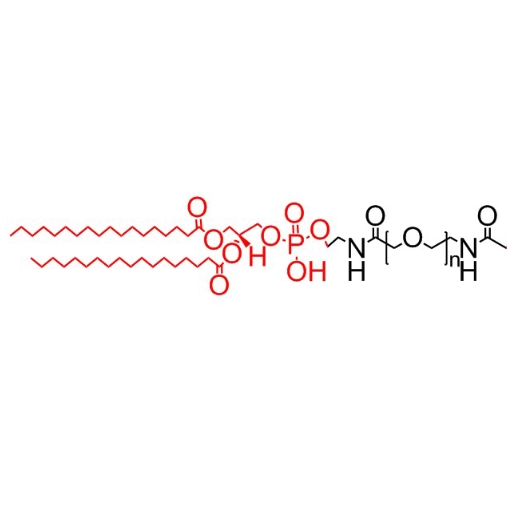
图:DSPE-PEG结构式
DSPE-PEG可以通过改变PEG的分子量或对其进行化学修饰,可以调节DSPE-PEG的物理化学性质,从而优化化合物的装载、释放和靶向性能。DSPE-PEG2000修饰的脂质体能够防止脂质体被免疫系统快速清除,不会被MPS捕获,并且可以通过调整脂质体的组成和结构来控制化合物在部位的释放,在体内循环过程中,化合物从脂质体中的缓慢释放可以延长化合物的作用时间,从而延长了脂质体在体内中的循环时间。
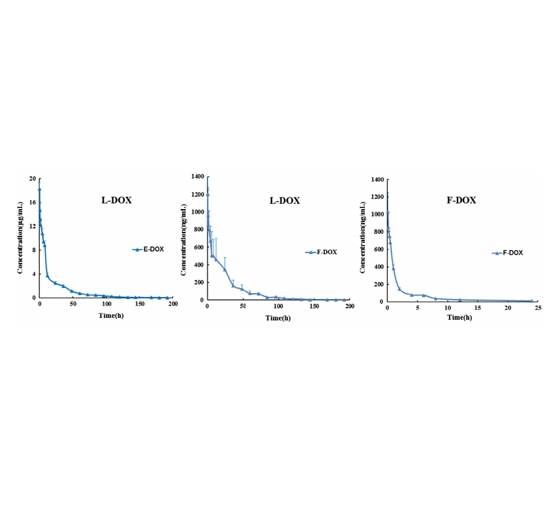
图:DOX或L-DOX给药后血浆中E-DOX和F-DOX的浓度-时间曲线
L-DOX的脂质组成为HSPC/胆固醇/DSPE-PEG2000。阿霉素脂质体通过远程加载制备,由跨膜硫酸铵梯度驱动。采用Sephadex G50尺寸排除柱测定DOX脂质体的封装效果。
结论:
DSPE-PEG2000修饰的脂质体能够影响化合物的消除速率和分布容积等化合物动力学参数,从而优化化合物的递送效果。这种靶向递送方式能够确保化合物更准确地传递到目标细胞或组织,从而提高化合物的效果并减少副作用。

 2024-12-18 作者:ws 来源:
2024-12-18 作者:ws 来源:

