文献:Resveratrol-modified mesoporous silica nanoparticle for tumor-targeted therapy of gastric cancer
文献链接:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34506231/
作者:Mingzhen Lin, Wenxia Yao, Yao Xiao, Zhijie Dong, Wei Huang, Fan Zhang, Xinke Zhou & Min Liang
相关产品:单分散二氧化硅
原文摘要:Resveratrol (Res) has been shown to exhibit anti-cancer properties in gastric cancer. However, its clinical application is limited by its poor pharmacokinetics, stability, and low solubility. Hence, this study aimed to explore and verify a better delivery system for gastric cancer therapy. Using transmission electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, and ultraviolet (UV) spectrometry, we observed the shape and encapsulation of resveratrol-modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSN-Res) that were synthesized by chemical methods. To explore the anticancer effects of these MSN-Res in vivo and in vitro, we established AGS and HGC-27 tumorbearing mouse models. Meanwhile, the proliferation of gastric cancer cells in vitro and in vivo was assessed by Cell Counting Kit-8, EdU, and Ki-67 immunohistochemical staining methods, while cellular apoptosis, and invasion and migration were detected by TdT-mediated dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) and Transwell assays, respectively. FTIR and UV results showed that we successfully synthesized and loaded drugs. Safety evaluation experiments showed that neither MSN-SH nor MSN-Res had toxic effects on the normal tissues of animals. Moreover, in vitro experiments revealed that MSN-Res significantly inhibited the proliferation, invasion, and migration of gastric cancer cells. Furthermore, TUNEL assay showed that MSN-Res promoted apoptosis in gastric cancer. These results were confirmed by the nude mouse tumorigenesis experiment. In conclusion, we demonstrated that MSN-Res showed better inhibitory effect on the development of gastric cancer than Res alone, indicating that MSN-Res could be a promising drug delivery system for gastric cancer treatment.
白藜芦醇(Res)具有抗cancer作用。但由于其药代动力学差、稳定性差和溶解度低,因此,探索和验证一种较好的胃cancer给药系统。利用透射电子显微镜、傅里叶变换红外(FTIR)光谱和紫外(UV)光谱,观察了化学方法合成的白藜芦醇修饰介孔二氧化硅纳米颗粒(MSN-Res)的形状和封装情况。MSN-SH和MSN-Res对动物的正常组织均无害。此外,MSN-Res可抑制胃cancer细胞的增殖、侵袭和迁移。TUNEL检测结果显示,MSN-Res可促进胃cancer细胞Apoptosis 。
单分散二氧化硅,依次用官能基团-SH和-SHCOOH进行修饰,然后将Res加载到修饰后的单分散二氧化硅表面,用PEI-FA按照方法进行修饰。将十六烷基三甲基溴化铵(CTAB)和氢氧化钠加入到去离子水中,然后加热。然后,在溶液中缓慢加入正硅酸四乙酯、3-巯基丙基三甲氧基硅烷(MPTMS)保存。将得到的MSN-SH用蒸馏水和乙醇洗涤,真空干燥,然后,通过允许MSN-SH与Py-SSPy、二甲基甲酰胺(DMF)、 3-巯基丙酸和乙酸反应得到MSN-SHCOOH。超声将改性MSN-SHCOOH重悬于含res无水乙醇中,在黑暗中搅拌,装载res的单分散二氧化硅离心后用乙醇和水洗涤。将RES的MSN与PEI-FA偶联,得到MSN/Res-PEI-FA。
利用透射电镜(TEM)观察了res修饰的单分散二氧化硅的亚定位。装载res的单分散二纳米硅用戊二醛溶液固定,然后用预冷磷酸盐缓冲盐水冲洗。然后,用的四氧化锇和碳酸钙缓冲液将细胞后固定,然后在室温下干燥。傅里叶变换红外(FTIR)光谱法,确定了不同官能团和Res的二分散二氧化硅的掺入和吸收峰。
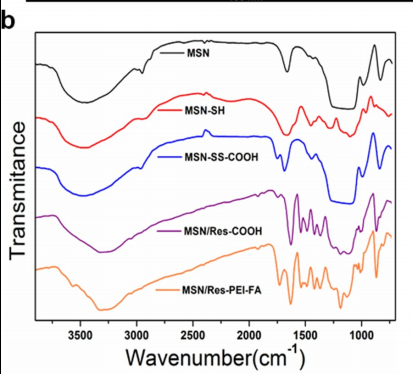
图:(FTIR)光谱法检测不同表面改性的单分散二氧化硅的振动峰
结论:单分散二氧化硅具有高载药能力、良好的生物相容性和易于表面修饰。它们也有可调节的孔径,这允许控制药物释放。研究成功地制备了res修饰的单分散二氧化硅,并对其特性进行了表征。功能分析表明,Res修饰的单分散二氧化硅Treatment 胃cancer的抗tumor作用优于单独修饰的Res,并成功实现了Res满载功能化单分散二纳米硅,吸附在细胞表面而不破坏细胞膜或细胞形态,具有较高的生物安全性。

 2024-12-18 作者:ZJ 来源:
2024-12-18 作者:ZJ 来源:

