文献:Multifunctional Immunoliposomes Combining Catalase and PD-L1 Antibodies Overcome Tumor Hypoxia and Enhance Immunotherapeutic Effects Against Melanoma
文献链接:https://www.cqvip.com/doc/journal/3433231290
作者:Hei YTeng BZeng ZZhang SLi QPan JLuo ZXiong CWei S
相关产品:DSPE-Hyd-PEG2000-NHS 磷脂-腙键-聚乙二醇2000-活性酯
原文摘要:Yu Hei,1 Binhong Teng,2,3 Ziqian Zeng,2,3 Siqi Zhang,3 Qian Li,3 Jijia Pan,3 Zuyuan Luo,3 Chunyang Xiong,1 Shicheng Wei2,3 1Department of Mechanics and Engineering Science, College of Engineering, Peking University, Beijing, People’s Republic of China;2Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, School and Hospital of Stomatology, Peking University, Beijing, People’s Republic of China;3Laboratory of Biomaterials and Regenerative Medicine, Academy for Advanced Interdisciplinary Studies, Peking University, Beijing, People’s Republic of ChinaCorrespondence: Chunyang XiongDepartment of Mechanics and Engineering Science, College of Engineering, Peking University, Beijing, People’s Republic of ChinaTel +86 10 62757940Email cyxiong@pku.edu.cnShicheng WeiDepartment of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, School and Hospital of Stomatology, Peking University, Beijing, People’s Republic of ChinaTel +86 10 82195780Email sc-wei@pku.edu.cnBackground: Immune checkpoint blockades (ICBs) are a promising treatment for cancers such as melanoma by blocking important inhibitory pathways that enable tumor cells to evade immune attack. Programmed death ligand 1 monoclonal antibodies (aPDL1s) can be used as an ICB to significantly enhance the effectiveness of tumor immunotherapy by blocking the PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitory pathway. However, the effectiveness of aPDL1s may be limited by low selectivity in vivo and immunosuppressed tumor microenvironment including hypoxia.Purpose: To overcome the limitations, we develop a multifunctional immunoliposome, called CAT@aPDL1-SSL, with catalase (CAT) encapsulated inside to overcome tumor hypoxia and aPDL1s modified on the surface to enhance immunotherapeutic effects against melanoma.Methods: The multifunctional immunoliposomes (CAT@aPDL1-SSLs) are prepared using the film dispersion/post-insertion method. The efficacy of CAT@aPDL1-SSLs is verified by multiple experiments in vivo and in vitro.Results: The results of this study suggest that the multifunctional immunoliposomes preserve and protect the enzyme activity of CAT and ameliorate tumor hypoxia. Moreover, the enhanced cellular uptake of CAT@aPDL1-SSLs in vitro and their in vivo biodistribution suggest that CAT@aPDL1-SSLs have great targeting ability,resulting in improved delivery and accumulation of immunoliposomes in tumor tissue.Finally, by activating and increasing the infiltration of CD8+ T cells at the tumor site, CAT@aPDL1-SSLs inhibit the growth of tumor and prolong survival time of mice,with low systemic toxicity.Conclusion: In conclusion, the multifunctional immunoliposomes developed and proposed in this study are a promising candidate for melanoma immunotherapy, and could potentially be combined with other cancer therapies like radiotherapy and chemotherapy to produce positive outcomes.Keywords: immunotherapy, programmed death ligand 1 monoclonal antibodies, aPDL1s, tumor hypoxia, melanoma, liposomes
该论文研究探索了一种DSPE-Hyd-PEG2000-NHS的物质在多功能免疫脂质体上的应用,通过结合过氧化氢酶和PD-L1抗体克服tumour缺氧,并增强对melanoma的免疫效果。
melanoma是一种特定环境中存在的低氧条件限制了免疫疗法的有效性。因此利用DSPE-hydrazone (Hyd)-PEG2000-NHS作为载体,在免疫脂质体上结合过氧化氢酶和PD-L1抗体,以克服tumour缺氧并增强免疫效果。
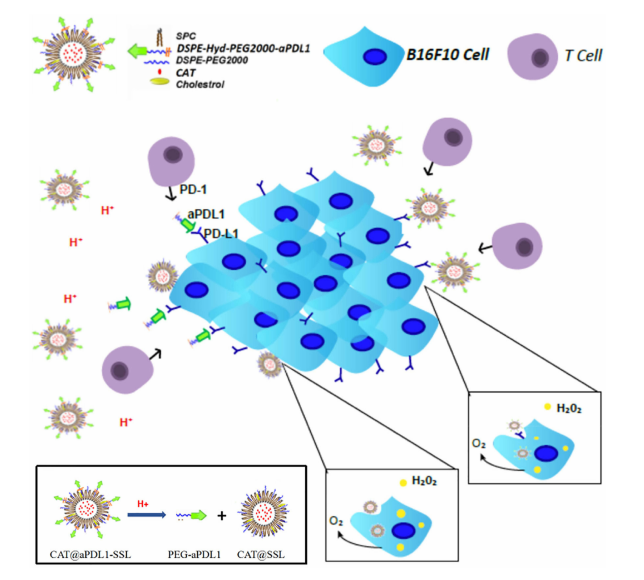
图1:CAT@aPDL1-SSL的结构及激活机制示意图。
实验结果显示,DSPE-hydrazone (Hyd)-PEG2000-NHS能够稳定地结合到免疫脂质体上,并释放出过氧化氢酶和PD-L1抗体。过氧化氢酶可以降解tumour细胞内的过氧化物,从而改善tumour缺氧状态。PD-L1抗体可以阻断tumour细胞上的PD-L1信号通路,激活机体的免疫系统,增强免疫细胞对tumour的攻击能力。
在体外实验中,发现这种多功能免疫脂质体能够抑制melanoma细胞的生长和增殖。而在小鼠实验中,使用DSPE-hydrazone (Hyd)-PEG2000-NHS载体的免疫脂质体方案使tumour生长受到有效控制,并且增强了小鼠的免疫系统对melanoma的攻击能力。
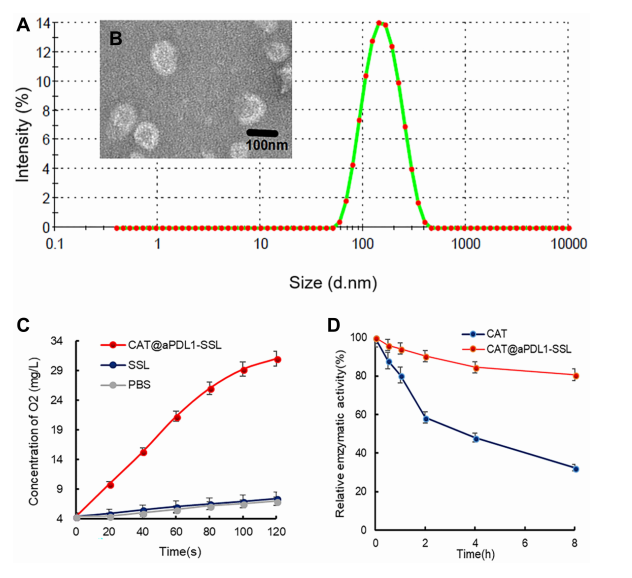
图2:CAT@aPDL1-SSLs的表征。
结论:SPE-hydrazone (Hyd)-PEG2000-NHS在多功能免疫脂质体中发挥了重要作用。该分子通过有效连接催化酶和PD-L1抗体,增强了脂质体的靶向性和生物相容性。DSPE的疏水性部分确保了脂质体的稳定性,而PEG2000部分则提供了良好的循环特性,有助于避免免疫清除。Hydrazone链接能够在tumour微环境中断裂,释放催化酶以降低tumour内的缺氧水平,从而提高效果。

 2025-06-06 作者:wff 来源:
2025-06-06 作者:wff 来源:

