文献:Swellable Silk Fibroin Microneedles for Transdermal Drug Delivery
文献链接:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28778522/
作者:Zhuping Yin, Dajiang Kuang, Shiyi Wang, Zhaozhu ,Zheng, Vamsi K. Yadavalli, Shenzhou Lu
相关产品:FITC-Dextran
原文摘要:
In this paper, a swelling-modified silk fibroin (SF) microneedle for transdermal
drug delivery is presented. The microneedles undergo a phase transition from a dried and 2rigid state to a semi-solid, acerose hydrogel state with a controlled 3-dimensional (3D) porous network structure. Different micromolecular reagents have been studied for mixing with aqueous silk fibroin to endow a swellable and insoluble capacity to the SF. The aqueous SF composite is poured on a polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) mold with arranged micropores on its surface to fabricate SF microneedles with high fidelity and mechanical robustness. The results demonstrate that 2-ethoxyethanol (ECS) modified SF microneedles can easily pierce porcine skin with a depth of ~200 μm in vitro, and transform into semi-solid hydrogels with
50 - 700 nm porous network inside. These swelling-modified microneedles can accomplish a significantly enhanced transdermal drug release capacity in proportion to their swelling characteristics. The better swelling capacity of the microneedles produces larger pores, resulting in higher transdermal drug release kinetics. There is also a relationship between swollen pore dimensions and the molecular weights of encapsulated therapeutics. The controllable properties of these SF microneedles coupled with their high biocompatibility, render swell-to-release ECS/SF composites as viable transdermal delivery devices.
膨胀修饰丝纤维素(SF)微针从干燥和刚性状态到半固态,酰聚糖水凝胶状态,具有可控的三维(3D)多孔网络结构。研究了不同的微分子试剂与丝素水混合,使SF具有可膨胀和不溶的能力。将SF复合材料倒在表面有微孔的聚二甲基硅氧烷(PDMS)模具上,以制造具有高保真度和机械鲁棒性的SF微针。
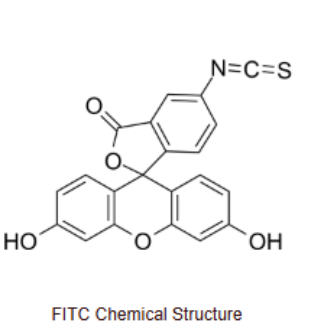
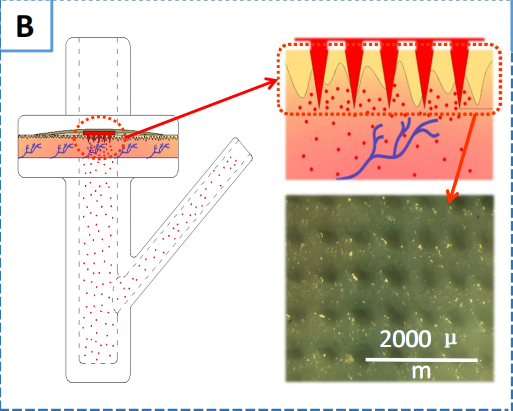
为了评估肿胀修饰的MNS的经皮传递特性,各种用荧光素异硫氰酸酯标记的异构体I(FITC-Dextran, Mw: 5 kDa, 10 kDa, 40 kDa)以1/20的比例作为模型代理,ECS改良MNS肿胀率分别为300、500、700 %,溶解纯SF MNS经体外经皮扩散,以相应的载化合物SF膜为对照组扩散。将载化合物的MNS应用于500 - 600 μm厚度的Pig carcass皮肤,然后用32 oC PBS(pH: 7.4,V = 13 ml)固定于TT-8透皮扩散装置(图B),每组4个平行样本。所有释放组在之前建立的时间点定期采样,然后进行荧光检测,使用FM4P-TCSPC荧光光谱分析仪监测FITC-葡聚糖的浓度(Ci),激发波长为495 nm,发射波长为516 nm。
结论:结果表明,2-乙氧基乙醇(ECS)改性SF微针在体外200 μm深度下容易穿透动物皮肤,转化为50 - 700 nm多孔网络的半固态水凝胶。这些膨胀修饰的微针可以根据其膨胀特性增强透皮化合物释放能力。微针较好的膨胀能力产生更大的孔隙,导致更高的透皮化合物释放动力学。肿胀的孔隙尺寸与封装Treatment 化合物的分子量之间也有关系。这些SF微针的可控特性加上它们高的生物相容性,使膨胀释放ECS/SF复合材料成为可行的透皮传递装置。

 2025-02-10 作者:ZJ 来源:
2025-02-10 作者:ZJ 来源:

