文献:Protective effect of Dioscorea zingiberensis ethanol extract on the disruption of blood–testes barrier in high-fat diet/ streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice by upregulating ZO-1 and Nrf2
文献链接:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31957918/
作者:Jie Zhou,Youli Xi,Jie Zhang,Jun Tang,Xiaowei Zhou,Jiayi Chen,Chao Nie, Zhengbiao Zhu,Bo Ma
相关产品:FITC-dextran 荧光素-葡萄糖
原文摘要:Testicular injury is the primary pathogenesis of diabetes-induced male infertility.
Dioscorea zingiberensis (DZ), a traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) including saponins, flavonoids and cellulose, is used to treat diseases in the reproductive system. But the protective effects of DZ on diabetes-induced testicular injury remain poorly understood. In this study, the therapeutic effects of chronic oral DZ treatment on testis impairment in a diabetic mouse model were explored by assessing sperm morphology, blood–testes barrier (BTB) integrity and testicular histological examination. Our results showed that DZ significantly reversed BTB disruption, testicular tissue injury and abnormal sperm morphology in diabetic mice. Interestingly, diabetes-induced disruption of the BTB was associated with a decrease in the tight junction (TJ) protein zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1). Dioscorea zingiberensis effectively increased ZO-1 expres
sion in testis tissue to restore the integrity of the BTB. Moreover, DZ treatment significantly reduced hyperglycaemia-induced increases in malondialdehyde (MDA) and 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) levels. Further mechanistic studies revealed that DZ substantially enhanced the expression of Nrf2, NOQ1 and HO-1, which indicated that DZ exerts potential antioxidant effects against testicular tissue damage via the activation of Nrf2. In conclusion, the protective effects of DZ rely on repairing the integrity of the BTB and on reducing oxidative stress damage by mediating ZO-1 and Nrf2. The study contributes to discovering the DZ possible mechanism of action.
FITC-dextran(异硫氰酸荧光素标记的葡聚糖)有诸多优点。FITC 的标记赋予了它荧光特性,在显微镜下可清晰观察,便于进行细胞摄取、组织分布等研究的可视化追踪。其二,葡聚糖具有良好的生物相容性,可安全地用于体内和体外实验。其三,不同分子量的葡聚糖可以满足不同的实验需求,例如小分子的可以快速透过某些屏障,大分子的则可用于模拟大分子物质在体内的运输情况。其四,稳定性高,不易被降解或变质,能够在较长时间内保持其荧光和化学性质。姜黄酮(DZ)是一种传统中化合物(TCM),包括皂苷、黄酮和纤维素,应用于生殖系统。基于此探讨慢性口服DZ的效果:
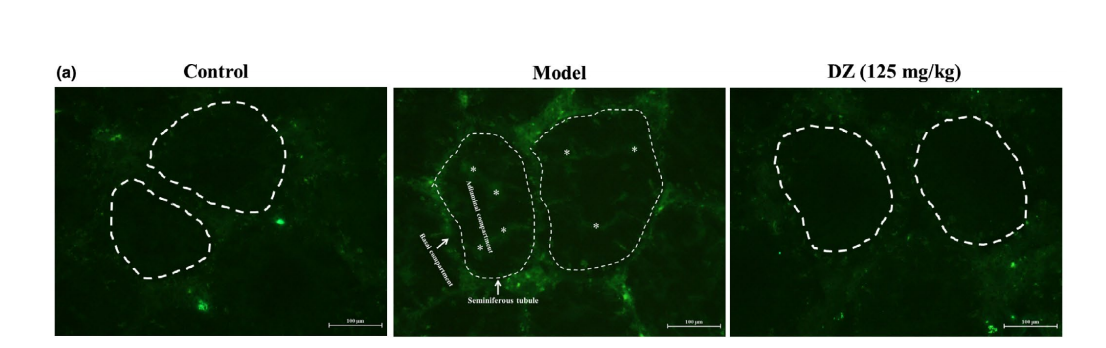
图:在DZ处理10周后,用FITC荧光示踪法检测小鼠BTB的通透性。(*)表明FITC从testicle组织中的精小管管腔室进入间质间隙。
采用荧光示踪方法评估小鼠的testicle屏障的完整性。在小鼠尾部静脉注射FITC-右旋糖酐后,取出右侧testicle,置于带有棕色埃彭多夫管中,作为冷冻切片。冷冻切片用低温恒温机切片,荧光染色切片用荧光显微镜检测。采用荧光示踪法来评价BTB的完整性。STZ/HFD诱导diabetes后,testicle腔间和间隙绿色FITC-葡聚糖荧光明显增强,说明BTB的通透性增加。在STZ/HFD诱导的diabetes模型中,DZTreatment 阻止了绿色荧光进入管腔内腔室。综上所述,DZ通过上调ZO-1,恢复了BTB的破坏。
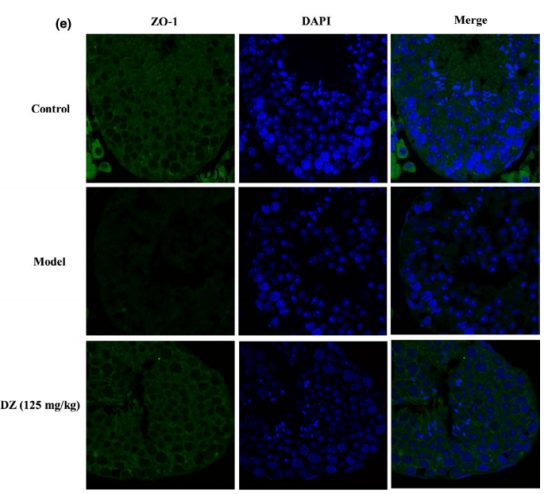
图:用IF(×1000)和ZO-1抗体(绿色)和DAPI(蓝色)检测ZO-1的表达。
结论:通过FITC-dextran的荧光成像可知:DZ逆转了diabetes小鼠的BTB破坏、testicle组织损伤和sperm形态异常。此外,DZTreatment 还降低了丙二醛(MDA)和8-羟基-2‘-脱氧鸟苷(8-OHdG)水平的升高。进一步的机制研究表明,DZ增强了Nrf2、NOQ1和HO-1的表达,这表明DZ通过激活Nrf2对testicle组织损伤具有潜在的抗氧化作用。

 2025-02-10 作者:ZJ 来源:
2025-02-10 作者:ZJ 来源:

