文献:
Carboxymethyl Dextran-Based Nanomicelle Coatings on Microarc Oxidized Titanium Surface for Percutaneous Implants: Drug Release, Antibacterial Properties, and Biocompatibility
文献链接:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1155/2022/9225647
作者:Weiliang Ye , Minghao Zhou , Luxuan Zhang , Jingwei Yu , Junjun Fan , Hongbo Wei
相关产品:
β-glycerophosphate sodium(β-甘油磷酸钠)
原文摘要:
Bacterial contamination and biofilm formation onpercutaneous implants can lead to device failure and be life-threatening. To solve this issue, we constructed a carboxymethyl dextran- (CMD-) based nanomicelle antibacterial coating on the microarc-oxidized titanium (MAO-Ti) surface (described in the supplementary file). The self-assembled CMD-based nanomicelles and octadecylamine (ODA) were developed as a drug carrier and loaded with minocycline (MC). The characterization and stability of the MC-loaded nanomicelles were determined. The surface roughness, hydrophilicity, and drug release property of the coatings were also investigated. Our findings showed that the cross-linked MC-loaded nanomicelles (MC@(ODA-CMD)CL) were more stable than the uncross-linked nanomicelles. Moreover, MC@(ODA-CMD)CL was successfully incorporated into the pores of MAO-Ti, which significantly increased the surface hydrophilicity of the coatings without influencing their surface roughness. In addition, the coatings demonstrated a sustained release time of 360 h, with a cumulative release rate reaching 86.6%. Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) was used to determine the antibacterial properties of the coatings, and human skin fibroblasts were seeded on them to investigate their biocompatibility. The results showed that the coatings significantly reduced the number of adhesive S. aureus and promoted the viability, adhesion, and morphology of the human skin fibroblasts compared to smooth titanium (S-Ti) sheets. In conclusion, MC-loaded CMD-based nanomicelles coated on MAO-Ti surface (MC@(ODA-CMD)CL-Ti) demonstrated sustained-release properties, excellent antibacterial properties and biocompatibility, and promising potential as coatings for percutaneous implants.
β-glycerophosphate sodium:β-甘油磷酸钠,化学名称为甘油磷酸钠,是一种有机磷酸盐化合物。它的化学式为C3H7Na2O6P,分子量约为 216.04。分子结构中含有甘油骨架,甘油的一个羟基被磷酸酯化,并且磷酸基团带有两个钠离子来平衡电荷。这种结构使得它具有良好的水溶性。
calcium acetate:醋酸钙,也称为乙酸钙。它是一种白色松散细粉,有轻微的乙酸气味。其分子量约为 158.17,熔点在 160℃左右。醋酸钙具有较好的水溶性,在水中会发生电离,产生钙离子和醋酸根离子。基于β-甘油磷酸钠、醋酸钙的相关性质,载有交联 MC 的纳米胶束 (MC@(ODA-CMD) CL )的合成如下:
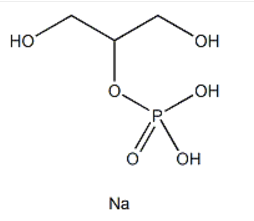
图:β-甘油磷酸钠结构式
钛试样(S-Ti、MAO-Ti、MC@(ODA-CMD)CL-Ti)的制备与表征:
商用纯钛片呈圆盘状,使用碳化硅纸机械研磨,并用丙酮、乙醇和去离子水进行超声波清洗。MAO实验在含有β-甘油磷酸钠和醋酸钙的混合电解液中进行,使用脉冲直流电源。然后,用去离子水冲洗标本表面并风干。将含有载药胶束加入明胶溶液中。超声处理形成悬浮液,滴加悬浮液均匀铺在钛片表面,摇匀,晾干。用乙醇清洗钛表面,冷冻干燥。采用扫描电镜观察S-Ti、MAO-Ti和MC@(ODA-CMD)CL-Ti的表面形貌。
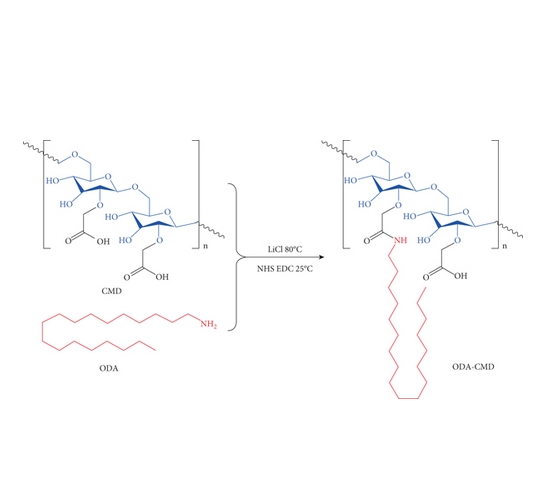
图:合成示意
结论:
该文献成功制备出基于β-甘油磷酸钠、醋酸钙合成的载有交联 MC 的纳米胶束 (MC@(ODA-CMD) CL )。结果表明,载有交联 MC 的纳米胶束 (MC@(ODA-CMD) CL ) 比未交联的纳米胶束更稳定。载有MC的CMD 基纳米胶束包覆在MAO-Ti 表面 (MC@(ODA-CMD) CL-Ti) 表现出缓释特性、良好的抗菌特性和生物相容性,以及作为经皮植入物涂层的潜力。

 2025-06-17 作者:ws 来源:
2025-06-17 作者:ws 来源:

