文献:Bioglass could increase cell membrane fluidity with ion products to develop its bioactivity
文献链接:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33043500/
作者:Longxin Yan,Haiyan Li,Weiliang Xia
相关产品:Liposomes 脂质体
原文摘要:
Objectives: Silicate bioactive glass (BG) has been widely demonstrated to stimulate both of the hard and soft tissue regeneration, in which ion products released from BG play important roles. However, the mechanism by which ion products act on cells on cells is unclear.
Materials and methods: Human umbilical vein endothelial cells and human bone marrow stromal cells were used in this study. Fluorescence recovery after photobleaching and generalized polarization was used to characterize changes in cell membrane fluidity. Migration, differentiation and apoptosis experiments were carried out. RNAand protein chip were detected. The signal cascade is simulated to evaluate the effect of increased cell membrane fluidity on signal transduction.
Results: We have demonstrated that ion products released from BG could effectively enhance cell membrane fluidity in a direct and physical way, and Si ions may play a major role. Bioactivities of BG ion products on cells, such as migration and differentiation, were regulated by membrane fluidity. Furthermore, we have proved that BG ion products could promote apoptosis of injured cells based on our conclusion that BG ion products increased membrane fluidity.
Conclusions: This study proved that BG ion products could develop its bioactivity on cells by directly enhancing cell membrane fluidity and subsequently affected cell behaviours, which may provide an explanation for the general bioactivities of silicate material.
脂质体的主要成分是磷脂,与生物膜的主要成分相似。它具有类似细胞膜的双层结构,内部为水相,可以包裹水溶性物质;而磷脂双分子层之间则可以容纳脂溶性物质。这种结构特点使得脂质体能够同时携带不同性质的药物、生物活性分子或其他物质。活性玻璃(BG)是一种典型的硅酸盐生物材料,通常由二氧化硅、氧化钙、五氧化二磷和氧化钠组成。BG的离子产物不仅能影响细胞行为,如细胞粘附、增殖、分化、极化,还能增强细胞间的相互作用,如细胞间的旁分泌作用和通过间隙连接的细胞通信。由于BG具有良好的溶解度,因此聚合物/BG复合支架和复合水凝胶等含BG的复合材料可以释放出相同的离子,并表现出与纯BG相同的生物效应。
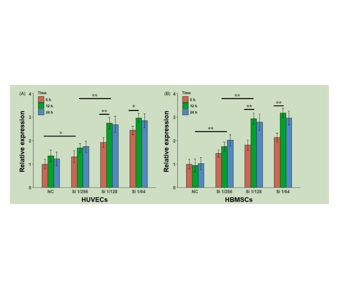
图为:含BG离子提取物(n = 3)刺激HUVECs和HBMSCs后Hsp70基因的表达。
脂质体在BG制备过程中的应用:
首先,脂质体可以作为载体来包裹和输送特定的成分进入 BG 的制备体系中。例如,可以将一些活性物质、催化剂或者特定的分子包裹在脂质体内部,通过控制脂质体的特性如大小、表面电荷等,实现对这些成分的准确输送和释放。在 BG 制备的特定阶段,脂质体可以将这些关键成分释放出来,促进反应的进行或者调节反应的进程。其次,脂质体的双层膜结构可以模拟生物膜的特性,为 BG 的形成提供一个类似于生物环境的微环境。这种微环境可以影响 BG 中分子的排列、聚集和相互作用方式。例如,在某些生物材料的制备中,脂质体可以帮助一些生物活性分子保持其活性构象,从而更好地参与到 BG 的形成过程中。此外,脂质体还可以作为稳定剂存在于 BG 的制备体系中。由于脂质体具有一定的表面活性,可以吸附在正在形成的 BG 颗粒表面,防止颗粒的聚集和沉淀,从而提高 BG 产品的稳定性和均匀性。
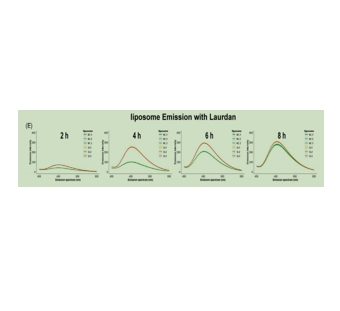
图为:劳丹混合脂质体的荧光发射峰
结论:
已经证明BG释放的离子产物可以直接和物理地提高细胞膜流动性,而硅离子可能发挥主要作用。BG离子产物在细胞上的生物活性,如迁移和分化,受膜流动性的调节。此外,基于BG离子产物增加了细胞膜的流动性的结论,BG离子产物可以促进损伤细胞的Apoptosis 。BG离子产物可以通过直接提高细胞膜流动性而影响细胞活性,从而提高细胞的生物活性,这可能为硅酸盐材料的一般生物活性提供了解释。

 2025-02-11 作者:lkr 来源:
2025-02-11 作者:lkr 来源:

