文献:Synergistic ultrasonic biophysical effect-responsive nanoparticles for enhanced
gene delivery to ovarian cancer stem cells
文献链接:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32627597/
作者:Chun Liufu , Yue Li , Yan Lin , Jinsui Yu , Meng Du , Yuhao Chen , Yaozhang Yang , Xiaojing Gong , Zhiyi Chen
相关产品:
DSPE-PEG2000-Biotin 磷脂-聚乙二醇2000-生物素
Biotin-PEG2000-SS-NHS 生物素-聚乙二醇2000-双硫键-活性酯
原文摘要:Ovarian cancer stem cells (OCSCs) that are a subpopulation within bulk tumor survive chemotherapy and conduce to chemo-resistance and tumor relapse. However, conventional gene delivery is unsuitable for the on-demand content release, which limits OCSCs therapeutic utility. Here, we reported ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction (UTMD)-triggerable poly(ethylene glycol)-disulfide bondpolyethylenimine loaded microbubble (PSP@MB). Taking advantage of glutathione (GSH) responsiveness, ultrasound triggering and spatiotemporally controlled release manner, PSP@MB is expected to realize local gene delivery for OCSCs treatment. But the biophysical mechanisms of gene delivery via PSP@MB and ultrasound remain unknown. The aim of this study is to determine the potential of gene delivery to OCSCs via ultrasonic synergistic biophysical effects and GSH-sensitive PSP@MB. The GSHsensitive disulfide bond cleavable properties of PSP@MB were confirmed by 1 H NMR spectra and infrared spectroscopy. The biophysical mechanisms between PSP@MB and cells were confirmed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM) to optimize the ultrasonic gene delivery system. The gene transfection via ultrasound and PSP@MB was closely related to the biophysical mechanisms (sonoporation, enhanced-endocytosis, sonoprinting, and endosomal escape). Ultrasound combined with PSP@MB successfully delivered aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 (ALDH1) short hairpin RNA (shRNA) plasmid to OCSCs and promoted apoptosis of OCSCs. The gene transfection rate and apoptosis rate were (18.41 ± 2.41)% and (32.62 ± 2.36)% analyzed by flow cytometry separately. This study showed that ultrasound triggering and GSH responsive PSP@MB might provide a novel strategy for OCSCs treatment via sonoporation and enhanced-endocytosis.
DSPE - PEG2000 - Biotin 是一种生物材料。DSPE 使其能够与细胞膜等生物膜结构产生相互作用,可构建脂质体等纳米载体。PEG2000 链段有效增加了材料的水溶性与空间位阻,减少蛋白质非特异性吸附,提升化合物或生物活性物质的传输稳定性与持久性。Biotin(生物素)可与多种生物素结合蛋白(如链霉亲和素、亲和素)特异性结合。通过生物素与亲和蛋白的特异性识别,能够准确地将负载化合物或检测探针的纳米载体导向特定细胞或组织靶点。基于此该文献报道了超声靶向微泡破坏(UTMD)-可触发聚(乙二醇)-二硫键聚乙烯亚胺装载的微泡(PSP@MB)。PSP@MB利用谷胱甘肽(GSH)反应性、超声触发和时空控制释放方式,实现OCSCs的局部基因传递。过程如下
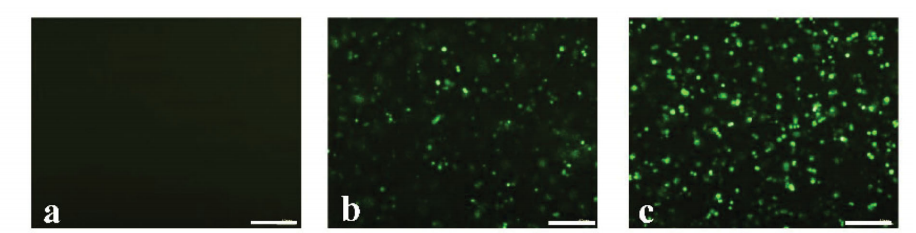
图:OCSC暴露于不同试剂编码的ALDH1 shRNA的含质粒后的荧光图像
PSP纳米颗粒和PSP@MB的制备
用PEI和生物素-PEG2000-SS-NHS制备了生物素化的PSP纳米颗粒。然后,用透析膜纯化生物素化的PSP纳米颗粒。采用薄膜水化法,用脂质壳(DPPC、DSPE-PEG2000-Biotin和DPTAP)和C3F8气芯制备生物素化的MBs。PSP@MB采用生物素化的PSP和生物素化的MB,采用生物素-亲和素法制备。用莫尔文和贝克曼库尔特测量了PSP纳米颗粒和PSP@MB的电位和直径。通过荧光显微镜和透射电子显微镜(TEM)对PSP@MB进行了验证。通过凝胶阻滞法分析了PSP纳米颗粒的DNA结合。
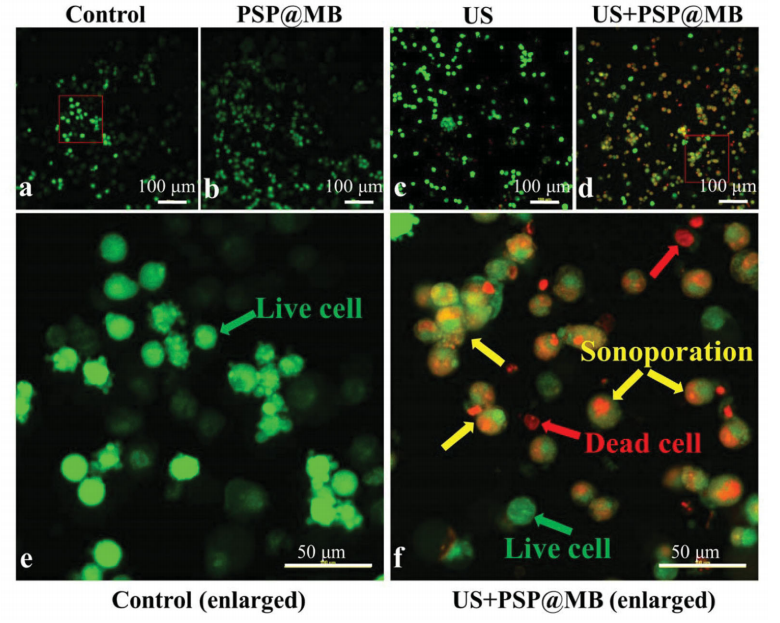
图:超声后,OCSCs中钙黄绿素(绿色)和PI(红色)的代表性共聚焦显微镜图像。
结论:通过1 H NMR和红外光谱,证实了DSPE - PEG2000 - Biotin参与制备的PSP@MB对GSH敏感的二硫键的可裂解性质。通过扫描电子显微镜(SEM)和共聚焦激光扫描显微镜(CLSM)确定了PSP@MB与细胞之间的生物物理机制,优化了超声基因传递系统。PSP@MB转染基因与其生物物理机制密切相关。超声结合PSP@MB成功地将醛脱氢酶1(ALDH1)短发夹RNA(shRNA)质粒递送到OCSCs中。

 2025-07-09 作者:ZJ 来源:
2025-07-09 作者:ZJ 来源:

