文献:Reactive oxygen species-responsive dexamethasone-loaded nanoparticles for targeted treatment of rheumatoid arthritis via suppressing the iRhom2/TNF-α/BAFF signaling pathway
文献链接:
https://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/8d21f8559e565480dddd3a215ba000a8
作者:Rongrong Ni, Guojing Song, Xiaohong Fu, Ruifeng Song, Lanlan Li, Wendan Pu, Jining Gao, Jun Hu, Qin Liu, Fengtian He, Dinglin Zhang, Gang Huang
相关产品:
DSPE-PEG 磷脂-聚乙二醇
DSPE-PEG-FA 磷脂-聚乙二醇-叶酸
原文摘要:Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an immune-mediated inflammatory disease that results in synovitis, cartilage destruction, and even loss of joint function. The frequent and long-term administration of anti-rheumatic drugs often leads to obvious adverse effects and patient non-compliance. Therefore, to specifically deliver dexamethasone (Dex) to inflamed joints and reduce the administration frequency of Dex, we developed Dex-loaded reactive oxygen species (ROS)-responsive nanoparticles (Dex/Oxi-αCD NPs) and folic acid (FA) modified Dex/Oxi-αCD NPs (Dex/FA-Oxi-αCD NPs) and validated their anti-inflammatory effect in vitro and in vivo. In vitro study demonstrated that these NPs can be effectively internalized by activated macrophages and the released Dex from NPs significantly downregulated the expression of iRhom2, TNF-α, and BAFF in activated Raw264.7. In vivo experiments revealed that Dex/Oxi-αCD NPs, especially Dex/FA-Oxi-αCD NPs significantly accumulated at inflamed joints in collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) mice and alleviated the joint swelling and cartilage destruction. Importantly, the expression of iRhom2, TNF-α, and BAFF in the joint was inhibited by intravenous injection of Dex/Oxi-αCD NPs and Dex/FA-Oxi-αCD NPs. Collectively, our data revealed that Dex-loaded ROS-responsive NPs can target inflamed joints and attenuate arthritis, and the ‘iRhom2-TNF-α-BAFF’ pathway plays an important role in the treatment of RA with the NPs, suggesting that this pathway may be a novel target for RA therapy.
DSPE-PEG2000 和 DSPE-PEG2000-FA 是具有特定结构和性能的化合物,DSPE-PEG2000由二硬脂酰磷脂酰乙醇胺(DSPE)、聚乙二醇(PEG)2000 组成。DSPE 部分具有亲脂性,可与脂质膜相互作用;PEG2000 具有亲水性,形成水化层。纳米粒子制备中,DSPE-PEG2000 可在纳米粒子表面形成稳定的涂层,防止粒子聚集和沉淀。DSPE-PEG2000-FA在 DSPE-PEG2000 的基础上连接了叶酸(FA),兼具 DSPE-PEG2000 的特性以及叶酸的靶向功能。该文献介绍了Dex/Oxi-αCD NPs由地塞米松(Dex)作为药物负载,通过特定的合成方法与活性氧(ROS)响应型材料(如Oxi-αCD)结合形成纳米粒子。这种结构使得Dex/Oxi-αCD NPs能够在ROS存在的情况下响应并释放药物。DSPE-PEG2000 和 DSPE-PEG2000-FA在Dex/Oxi-αCD NPs制备和表征中有应用,具体如下:
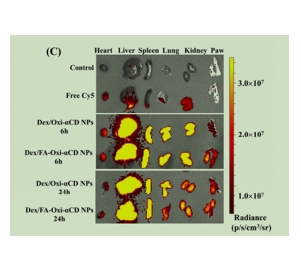 图为:Cy5标记的Dex/Oxi-αCD NPs的荧光强度
图为:Cy5标记的Dex/Oxi-αCD NPs的荧光强度
DSPE-PEG2000和DSPE-PEG2000-FA在响应纳米颗粒Dex/Oxi-aCD NPS制备及表征中的应用:
采用改良的纳米沉淀/自组装方法制备了Dex/Oxi-aCD NPS。简要地说:将DSPE-PEG2000和卵磷脂分散在无水乙醇中,然后向分散液中加入去离子水。在轻微搅拌下,将水分散液加热至。随后,在搅拌下,向预热后的脂质分散溶液中逐滴加入Dex和Oxi-aCD的甲醇溶液,再涡旋。将混合物冷却至室温并自组装。收集凝固的NPS洗涤,然后悬浮在超纯水中。为了制备FA修饰的Dex/0xi-aCD NPS(命名为Dex/FA-0xi-aCDNPS),在水性分散体中添加了磷脂酰胆碱、的DSPE-PEG2000和DSPE-PEG2000-FA。通过类似的方法,制备了不含Dex的空载Oxi-aCD NPS。或者,使用Cy5偶联的Oxi-aCD制备Cy5标记的Oxi-aCD。
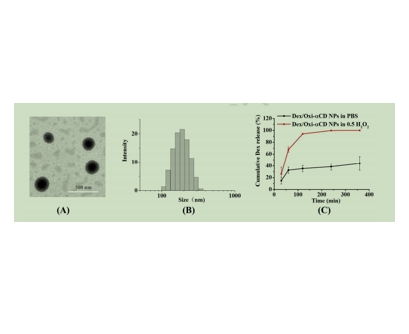
图为:Dex/Oxi-αCD NPs的表征
结论:DSPE-PEG2000和DSPE-PEG2000-FA在响应纳米颗粒Dex/Oxi-aCD NPs的制备及表征中发挥着重要作用。DSPE-PEG2000经常用于脂质体的制备中,脂质体是一种用于药物传递系统和作为生物膜模型的基于脂质的小囊泡。在Dex/Oxi-aCD NPs的制备中,DSPE-PEG2000可以作为表面修饰剂,形成一层PEG外壳,从而增强纳米颗粒的稳定性和生物相容性。DSPE-PEG2000-FA可以作为靶向配体,与Dex/Oxi-aCD NPs结合,形成具有靶向递送能力的纳米颗粒。通过叶酸与叶酸受体的高亲和力结合,DSPE-PEG2000-FA修饰的纳米颗粒可以实现对特定细胞或组织的靶向递送。

 2025-07-14 作者:lkr 来源:
2025-07-14 作者:lkr 来源:

