文献:Macrophage-biomimetic liposomes delivery of carbon dots nanozymes ameliorate ulcerative colitis by modulating inflammation pathways and remodeling the redox microenvironment
文献链接:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1385894723055274
作者:Yana Ma , Jingjie Zhao , Zhichao Deng , Bowen Gao , Chenxi Xu , Xiangji Yan , Mei Yang , Yujie Zhang , Qiuran Xu , Mingzhen Zhang , Changlong Xu
相关产品:DOTAP(1,2-二油酰- 3 -三甲铵丙烷)
原文摘要:
As a recurrent chronic inflammatory intestinal disease, ulcerative colitis (UC) has seriously affected the life quality of patients. Numerous studies have demonstrated excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS) are involved in the occurrence and development of UC, and manipulating ROS expression in the intestinal microenvironment to lower the redox signaling and oxidative stress is a promising strategy in UC therapeutics. We previously demonstrated that carbon-dots (C-dots) nanozymes with superoxide dismutase-like activity could effectively clear ROS and alleviate inflammation, while the accurate lesion location targeting is still a crucial factor in impacting their therapeutic efficiency. In this study, inspired by naturally occurring intercellular interactions, macrophage cell membrane-coated liposomes were constructed to deliver C-dots to amplify their efficiency. The obtained C-dots@Lipo-M endowed C-dots with prolonged circulation time and inflammation targeting capability. In addition, this delivery platform could be co-localized with mitochondria where ROS generated. In dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced UC models, C-dots@Lipo-M exerted satisfactory preventive and therapeutic effects on colitis by reversing the shortened colon length, scavenging ROS, decreasing the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and reducing barrier protein expression at colon sites. Further transcriptome sequencing revealed that C-dots@Lipo-M might alleviate intestinal inflammation by modulating inflammation pathways and remodeling the redox microenvironment. Collectively, this study provides a new targeted strategy to improve nanozymes therapeutic efficiency and extends their biomedical applications on inflammation-related diseases.
DOTAP:DOTAP 即 1,2 - 二油酰 - 3 - 三甲铵丙烷(1,2 - Dioleoyl - 3 - Trimethylammonium - Propane),是一种阳离子脂质。它主要由一个甘油骨架构成,在甘油的 1 位和 2 位连接着油酰基(一种不饱和脂肪酸基团),在甘油的 3 位连接着三甲铵丙烷基团。这种结构使其具有亲水性的头部(三甲铵丙烷部分)和疏水性的尾部(两个油酰基部分),属于两性分子。
基于DOTAP的性能,C-dots@Lipo-M的合成如下:
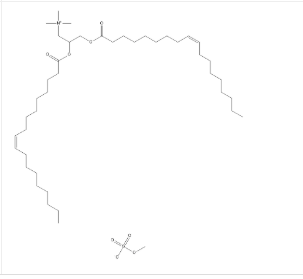
图:DOTAP结构式
C-dots@Lipo-M的制备:
按照一定的摩尔比称取 DOTAP 以及其他脂质成分,置于圆底烧瓶中,加入适量的有机溶剂,使脂质完全溶解,形成均匀的脂质溶液。将圆底烧瓶连接至旋转蒸发仪上,在一定温度下,缓慢旋转蒸发有机溶剂,脂质成分会在烧瓶内壁形成一层均匀的脂质薄膜。向含有脂质薄膜的烧瓶中加入适量的缓冲溶液,使脂质薄膜充分水合。接着将水合后的体系置于超声仪中进行超声处理,若采用水浴超声,通过超声使脂质体分散均匀,初步形成空白脂质体。将制备好的碳量子点(C-dots)溶液以及待包载的物质 M缓慢加入到上述分散好的空白脂质体溶液中,轻轻搅拌混合均匀。为促进包载过程,可以再次进行超声处理,使碳量子点和物质 M 更好地被包载进脂质体中,形成 C-dots@Lipo-M 复合物。将含有 C-dots@Lipo-M 复合物的溶液转移至高速离心机中,设定合适的转速和离心时间进行离心,使未包载进去的碳量子点、物质 M 以及一些杂质沉淀或分层,收集上清液,上清液中即为初步纯化的 C-dots@Lipo-M 复合物。
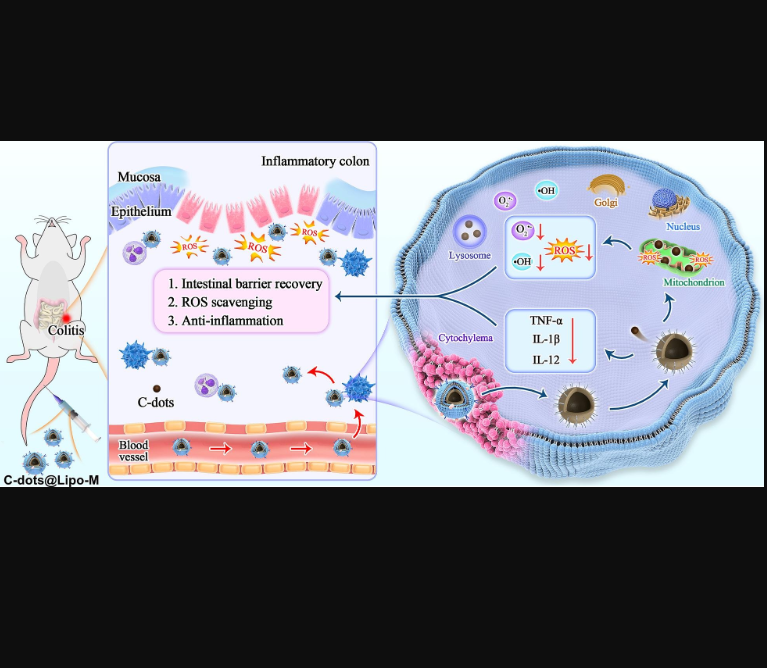
图:机制示意
结论:
该文献成功制备出基于DOTAP合成的复合物C-dots@Lipo-M。获得的C-dots@Lipo-M赋予C-dots能够延长的循环时间和Inflammation靶向能力,该复合物通过逆转缩短的结肠长度、清除ROS、减少促炎细胞因子的表达、减少屏障蛋白,对结肠炎发挥了预防和Treatment 作用。

 2025-07-29 作者:ws 来源:
2025-07-29 作者:ws 来源:

