文献:Chitosan oligosaccharide decorated liposomes combined with TH302 for photodynamic therapy in triple negative breast cancer
文献链接:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34011362/
作者:Yinan Ding, Rui Yang, Weiping Yu, Chunmei Hu, Zhiyuan Zhang, Dongfang Liu, Yanli An, Xihui Wang, Chen He, Peidang Liu, Qiusha Tang,Daozhen Chen
相关产品:
CO-FITC FITC标记的壳寡糖
FITC-CO-HPPH-TH302/Lipo 异硫氰酸荧光素-羰基-光敏剂-替拉扎明 / 脂质体
原文摘要:
Background: Triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) is an aggressive tumor with extremely high mortality that results from its lack of efective therapeutic targets. As an adhesion molecule related to tumorigenesis and tumor metastasis, cluster of diferentiation-44 (also known as CD44) is overexpressed in TNBC. Moreover, CD44 can be efectively targeted by a specifc hyaluronic acid analog, namely, chitosan oligosaccharide (CO). In this study, a CO-coated liposome was designed, with Photochlor (HPPH) as the 660 nm light mediated photosensitizer and evofosfamide (also known as TH302) as the hypoxia-activated prodrug. The obtained liposomes can help diagnose TNBC by fuorescence imaging and produce antitumor therapy by synergetic photodynamic therapy (PDT) and chemotherapy.
Results: Compared with the nontargeted liposomes, the targeted liposomes exhibited good biocompatibility and targeting capability in vitro; in vivo, the targeted liposomes exhibited much better fuorescence imaging capability. Additionally, liposomes loaded with HPPH and TH302 showed signifcantly better antitumor efects than the other monotherapy groups both in vitro and in vivo.
Conclusion: The impressive synergistic antitumor efects, together with the superior fuorescence imaging capability, good biocompatibility and minor side efects confers the liposomes with potential for future translational research in the diagnosis and CD44-overexpressing cancer therapy, especially TNBC.
CHO-FITC是由胆固醇基团和荧光素基团通过特定的化学键连接而成的化合物。这种结构使得荧光素基团能够在特定波长下发射荧光信号,从而实现对胆固醇的追踪和观察。CHO-FITC在特定波长光的激发下能够发出明亮的荧光信号,这使得它成为研究胆固醇在生物体内分布和动态变化的理想工具。CHO-FITC常被用作荧光探针来研究细胞膜中胆固醇的分布和溶解度变化。通过荧光显微镜,可以直观地观察到胆固醇在细胞内的分布、转运和代谢情况,从而深入了解胆固醇与各种疾病的关系。CO-FITC 在体外细胞摄取研究中发挥着重要作用,为深入理解细胞摄取机制、优化化合物递送系统以及开展相关的生物学研究提供了有力的工具。
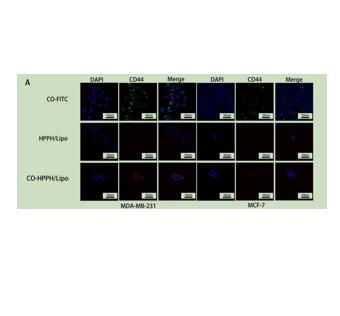
图为:分别用CO-FITC、HPPH/Lipo(即非靶向组)和CO-HPPH/Lipo(即靶向组)处理MDA-MB-231和MCF-7细胞。
CO-FITC在体外细胞摄取中的应用:
纳米颗粒的靶向能力对生物医学应用至关重要。检查CO-HPPH-TH302/脂肪体外CD44过表达tumor的结合能力,TNBC细胞系MDA-MB-231作为实验组,和non-TNBC细胞系MCF-7CD44阻断MCF-7细胞和CD44阻塞MDA-MB-231细胞作为对照组CD44表达低于实验组。与不含CO的脂质体相比,不含CO的脂质体可以提高脂质体的细胞摄取能力。CO几乎没有出现在被抗cd44抗体阻断的细胞表面。Te结果进一步证实了CO可以单独靶向CD44。此外,CO-HPPH-TH302/Lipo可以单独靶向TNBC,并进一步证实了CO已经成功地与脂质体连接。为了进一步评估靶向性和非靶向脂质体,进行了荧光细胞术,并测量了荧光强度。细胞摄取实验的Te结果表明,CO可以成功地与脂质体相连,并可以靶向过表达cd44的细胞。
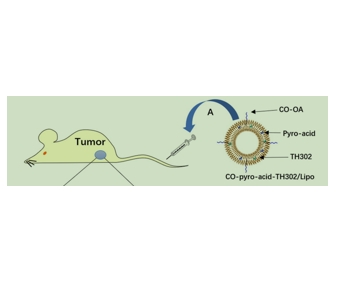
图为:经尾静脉静脉注射CO-HPPH-TH302/Lipo
结论:利用荧光分光光度计等仪器,可以对细胞摄取的 CO-FITC 进行定量检测。通过测量荧光强度,可以确定不同条件下细胞对标记物的摄取量,从而比较不同细胞系、不同处理条件或不同时间点的细胞摄取效率。这有助于筛选出具有高效摄取能力的细胞类型或优化细胞摄取的条件。CO-FITC 发出的荧光可以员在显微镜下直接观察到细胞摄取的动态过程。通过荧光显微镜或共聚焦显微镜,可以清晰地看到标记有 CO-FITC 的物质是如何进入细胞的,包括进入的途径、在细胞内的分布位置等。这为深入了解细胞摄取机制提供了直观的视觉证据。

 2025-07-29 作者:lkr 来源:
2025-07-29 作者:lkr 来源:

