文献:Soft Mesoporous Organosilica Nanoplatforms Improve Blood Circulation, Tumor Accumulation/ Penetration, and Photodynamic Efcacy
文献链接:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40820-020-00465-7
作者:Xin Peng, Kun Chen, Wanhua Liu, Xiongfeng Cao, Mengru Wang, Jun Tao, Ying Tian, Lei Bao, Guangming Lu, Zhaogang Teng
原文摘要:To date, the ability of nanoplatforms to achieve excellent therapeutic responses is hindered by short blood circulation and limited tumor accumulation/ penetration. Herein, a soft mesoporous organosilica nanoplatform modifed with hyaluronic acid and cyanine 5.5 are prepared, denoted SMONs-HA-Cy5.5, and comparative studies between SMONs-HA-Cy5.5 (24.2 MPa) and stif counterparts (79.2 MPa) are conducted. Results indicate that, apart from exhibiting a twofold increase in tumor cellular uptake, the soft nanoplatforms also display a remarkable pharmacokinetic advantage, resulting in considerably improved tumor accumulation. Moreover, SMONs-HA-Cy5.5 exhibits a signifcantly higher tumor penetration, achieving 30-μm deeper tissue permeability in multicellular spheroids relative to the stif counterparts. Results further reveal that the soft nanoplatforms have an easier extravasation from the tumor vessels, difuse farther in the dense extracellular matrix, and reach deeper tumor tissues compared to the stif ones. Specifcally, the soft nanoplatforms generate a 16-fold improvement (43 vs. 2.72 μm) in difusion distance in tumor parenchyma. Based on the signifcantly improved blood circulation and tumor accumulation/penetration, a soft therapeutic nanoplatform is constructed by loading photosensitizer chlorin e6 in SMONs-HA-Cy5.5. The resulting nanoplatform exhibits considerably higher therapeutic efcacy on tumors compared to the stif ones.
NH2-maleimide,即氨基-马来酰亚胺,是一种含有氨基(NH2)和马来酰亚胺基团的化学试剂。马来酰亚胺基团具有高度的反应活性,特别是在温和的条件下,能够与含有硫醇(SH)基团的化合物发生迈克尔加成反应,生成稳定的硫醚键。通常溶于有机溶剂,如二甲基亚砜(DMSO)、二甲基甲酰胺(DMF)等。在水中的溶解性可能因制备方法和纯度而异。在适当的储存条件下,NH2-MAL可以保持较长的稳定性。然而,长时间暴露在高温、光照或潮湿环境下可能导致其分解或失活。介孔有机氧化硅纳米颗粒(MONs)具有介孔结构、大的比表面积、易于功能化的表面以及方便掺杂各种有机基团的骨架。在生物医学领域,特别是刺激响应性药物释放、靶向药物输送等方面存在应用潜力。NH₂-maleimide 在制备氨基修饰的 MONs(介孔氧化硅纳米材料)中有重要应用,具体如下:
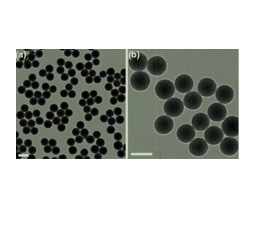
图为:MONs-HA-Cy5.5的TEM和c SEM图像
NH2-maleimide在制备氨基修饰的MONs中的的应用:
为了在MONs上嫁接氨基,形成硫醚桥接MONs的二硫键通过还原反应转化为硫醇基,然后与NH2-maleimide共价连接。简单地说,将MONs溶解在水、二恶烷、三苯基膦和盐酸溶液的混合物中。在氮气气氛中加热后,将另一种混合溶液离心得到连接MONs的硫醇基团,用水洗涤三次。随后,将沉淀物分散在水、 N、N-二甲基甲酰胺和NH2-maleimide的混合物中。室温摇晃,用水洗涤三次得到氨基修饰的MONs(MONs-nh2)。
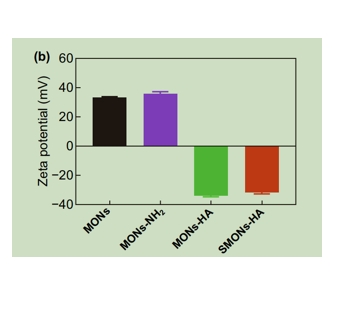
图为:MONs、MONs-NH2、MONs-HA和SMONs-HA的zeta电位
结论:NH₂-maleimide 分子中的马来酰亚胺基团可以与生物分子(如蛋白质、多肽等)上的巯基发生特异性反应,形成稳定的硫醚键;而其氨基则可以与 MONs 表面的活性基团(如羧基等)进行反应,从而将生物分子连接到 MONs 表面,实现对 MONs 的生物功能化修饰。在不同的 pH 环境下,NH₂-maleimide 的氨基和马来酰亚胺基团的反应活性可能会发生变化。利用这一特性,可以在 MONs 表面构建对 pH 敏感的刺激响应性系统。例如,在酸性条件下,氨基可能会发生质子化,从而影响其与马来酰亚胺基团的反应。

 2025-07-31 作者:lkr 来源:
2025-07-31 作者:lkr 来源:

