文献:Influence of Colonies’ Morphological Cues on Cellular Uptake Capacity of Nanoparticles
文献链接:
https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/bioengineering-and-biotechnology/articles/10.3389/fbioe.2022.922159/full
作者:Siyuan Huang , Qi Su , Xiaoqiang Hou , Kuankuan Han , Shufang Ma , Bingshe Xu , Yingjun Yang
相关产品:amino-modified fluorescent PS NPs(氨基修饰的荧光聚苯乙烯纳米粒子)
原文摘要:
High transmembrane delivery efficiency of nanoparticles has attracted substantial interest for biomedical applications. It has been proved that the desired physicochemical properties of nanoparticles were efficient for obtaining a high cellular uptake capacity. On the other hand, biophysical stimuli from in situ microenvironment were also indicated as another essential factor in the regulation of cellular uptake capacity. Unfortunately, the influence of colony morphology on cellular uptake capacity was rarely analyzed. In this study, micropatterned PDMS stencils containing circular holes of 800/1,200 μm in diameter were applied to control colonies’ size. The amino-modified nanoparticles were cocultured with micropatterned colonies to analyze the influence of colonies’ morphology on the cellular uptake capacity of nanoparticles. Consequently, more endocytosed nanoparticles in larger colonies were related with a bigger dose of nanoparticles within a larger area. Additionally, the high cell density decreased the membrane–nanoparticles’ contacting probability but enhanced clathrin-mediated endocytosis. With these contrary effects, the cells with medium cell density or located in the peripheral region of the micropatterned colonies showed a higher cellular uptake capacity of nanoparticles.
amino-modified fluorescent PS NPs:指氨基修饰的荧光聚苯乙烯纳米粒子(Polystyrene Nanoparticles)。主要由聚苯乙烯(PS)作为核心部分,以及修饰在其表面的氨基(-NH₂)和具有荧光性质的成分组成。聚苯乙烯是一种合成的聚合物,其化学结构是由苯乙烯单体聚合而成,这种聚合物为纳米粒子提供了基本的物理和化学稳定性,以及形状和尺寸的支撑。氨基则通过化学修饰的方式连接到聚苯乙烯纳米粒子的表面,它可以作为一种活性官能团,用于后续的化学反应,如与生物分子或其他功能分子的偶联。荧光成分的存在使纳米粒子能够发射出特定波长的荧光,用于检测、成像等多种应用。基于amino-modified fluorescent PS NPs的性能,介绍如下:
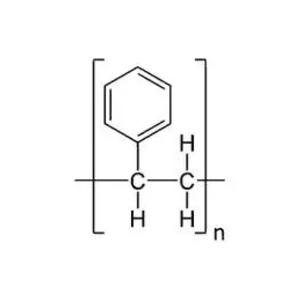
图:聚苯乙烯结构式
细胞摄取能力分析:
细胞播种一定时间后,将培养基替换为含有氨基修饰荧光PS NPs 的新鲜培养基,在加湿CO2培养箱中再孵育。收获样品,用台盼蓝孵育,灭灭细胞外NPs的荧光。最后,用多聚甲醛固定样品,用DAPI染色。用荧光显微镜观察并记录NPs和DAPI的荧光。计算np阳性细胞的百分比和荧光强度,评估细胞摄取能力。为了确定np阳性细胞,使用ImageJ计算每个细胞的综合灰度值(IGV)和面积(A)。为了得到校正后的IGV,选择没有细胞附着的区域作为背景,计算IGV背景和background。然后计算校正后的IGV。np阳性细胞定义为校正后的IGV比IGV背景值高两倍的细胞。np阳性细胞数除以总细胞数计算np阳性细胞百分比。纳米颗粒阳性细胞的校正IGV也被记录下来以评估细胞摄取能力。对每组荧光图像进行分析。
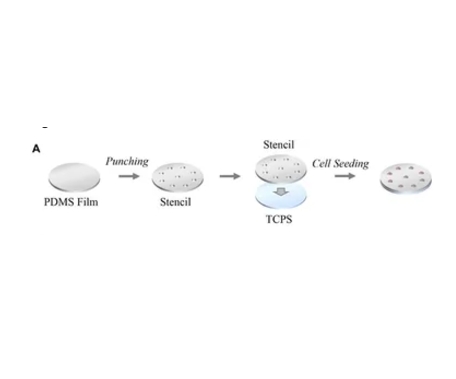
图:流程示意
结论:
该文献制备了PDMS模板,并将其应用于黑色素瘤菌落的形态学控制。随后,形态学线索对细胞摄取能力的影响被揭示。氨基修饰的荧光 PS NPs 可以模拟一些生物分子的性质和功能,从而用于研究细胞内的生理过程。其大小和表面性质与某些蛋白质或生物大分子相似,可以作为这些生物分子的模拟物,研究细胞对它们的摄取、运输和代谢过程,以及它们在细胞内的相互作用和功能发挥机制。

 2025-05-27 作者:ws 来源:
2025-05-27 作者:ws 来源:

